2024 Author: Josephine Shorter | [email protected]. Last modified: 2024-01-07 17:49
Melanoma: causes, symptoms, stages and diagnosis
Melanoma is a type of cancer that affects melanocytes. Melanocytes, in turn, are skin cells responsible for skin color.
Melanoma is prone to the rapid spread of metastases, which contributes to the formation of serious complications leading to death. In America alone, about 50,000 new melanoma patients are diagnosed each year.
Diagnostics, as a rule, is timely, since the patients themselves go to the doctor with characteristic complaints. After all, it is not difficult to identify melanoma, it is located in open areas of the body. The sooner a tumor is diagnosed, the higher the chance of recovery.
Content:
- Disease statistics
- Melanoma causes
- Types of melanomas
- Melanoma symptoms
- Melanoma stages
- What does melanoma look like?
- Melanoma diagnostics
- Disease prognosis
Disease statistics

In America and Australia, skin cancer ranks first among all cancers. In the rest of the world, this pathology is in the top three among the types of cancer, while it is melanoma that most often leads to the death of patients.
It has been established that every 60 minutes in the world, 1 patient dies from melanoma. In 2013, there were 77,000 registered melanoma patients. In this case, 9,500 patients died. The share of melanoma accounts for only 2.3% if we take cancer in general, but if we consider death from skin cancer due to melanoma, then this percentage is 75%.
In addition to the skin, melanoma can affect the eyes, scalp, and oral mucosa. At the same time, the age of a person and his gender have no effect on the incidence of the disease. It has been established that Caucasians have a 2% risk of developing melanoma, Europeans - 0.5%, and Africans - 0.1%.
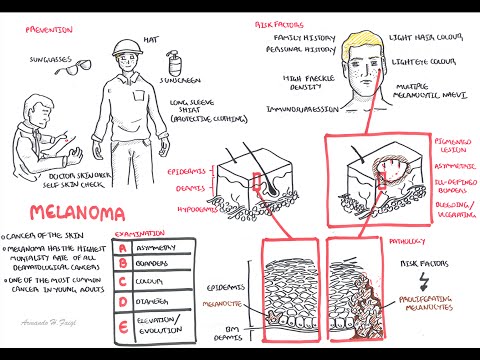
Melanoma causes
-
The negative effects of sunlight. Melanoma develops as a result of exposure to the skin of ultraviolet rays. This applies to getting a tan not only in the sun, but also in a solarium. The risk of developing melanoma is especially high if a person has been in the sun for a long time in childhood. The risk group includes residents of Australia, Florida, Hawaii, as the sun is overly active there.
Sunburns increase the risk of melanoma formation by 2 times, and visits to the solarium bring these risks up to 75%. Any equipment for creating tanning is classified by the WHO cancer research agency as a "risk factor for skin cancer." In addition, the equipment located in the solarium rooms is considered carcinogenic.
- The presence of atypical moles that rise above the skin and have an irregular shape increase the risk of developing this type of cancer. In addition, the more moles there are on the human body (and it does not matter what type they are), the higher the risk of developing the disease.
- The lighter a person's hair and eyes are, the higher their risk of melanoma formation.
- If there was a history of such a disease, then the risk of its recurrence increases.
-
Immunity dysfunction. Among the factors that increase the risk of developing melanoma: HIV, AIDS, organ transplantation, chemotherapy, etc.
You should also not exclude the factor of heredity. On average, every 10 patients diagnosed with melanoma have a close relative with the same disease. Complicated (the risk is close to 50%) is considered a family history if melanoma was in parents, sisters, brothers and children.
Types of melanomas
There are 4 types of melanoma. At the same time, 3 of them are characterized by gradual growth with damage to the surface layers of the skin, and one type has a tendency to rapid progression, grows into the deep layers of the skin and affects the internal organs.
-
Superficial or superficial melanoma. Most often, this type of disease is diagnosed in patients. The frequency of occurrence is equal to 70%. For a long time, the tumor remains benign and is localized in the surface layer of the skin. After a long time without any treatment, melanoma grows deeper. The first symptom of this type of tumor is the presence of a flat, asymmetrical spot with uneven boundaries. Moreover, its color can change, be black, white, red, brown, blue. Such melanomas often appear in the place where the mole is located. In men, it most often occurs on the trunk, in women on the lower limbs. On the back, this melanoma can occur with the same frequency in both sexes.
- Lentigo is malignant. This formation over a long period of time is located in the upper layers of the skin, has a flat, slightly raised shape, uneven color. Most often, such a spot is motley, with brown blotches. Mostly a similar tumor occurs in old age on those parts of the body that have been exposed to the sun more than others throughout their life. This is the face, arms, torso, ears. Malignant lentigo affects the inhabitants of Hawaii. When this type of melanoma grows, the disease is called lentigo-melanoma.
- Melanoma is nodular. Often, when such a tumor is found, it has already grown into the deep layers of the skin. This melanoma resembles a black or other colored bump. Most often, the tumor is located on the lower and upper limbs, or on the body. The frequency of occurrence is about 15%.
- Acral-lentiginous melanoma. First, it is located on the surface, without treatment it grows into the deep layers of the skin in the tissue. It can appear under the nails, on the feet and palms, it looks like a black or brown spot. The disease progresses rapidly compared to malignant lentigo and superficial melanoma. It is most often diagnosed in people with dark skin (in Asians and Africans), less often in Europeans and Caucasians.
Melanoma symptoms

Melanoma sometimes forms from a mole, and sometimes it occurs on healthy areas of the skin, or against the background of other skin diseases. Most often, the swelling appears on the lower limbs and on the upper back. In the overwhelming majority of cases, it has a dark color, since damaged cells produce melanin, but colorless formations can also occur.
The appearance of a tumor on the palms, on the nails, on the mucous membranes is possible. In old age, formations are most often localized on the face and neck, on the auricles and on the scalp.
The symptoms of melanoma are as follows:
Early symptoms of melanoma
If an existing mole or birthmark has changed its color and shape, it has become larger, it gives unpleasant sensations, then this may be a sign of melanoma. Moreover, changes often occur over a long period of time.
Sometimes a tumor is mistaken for a new mole, but its sloppy appearance should alert a person. All these changes are alarming symptoms and should be the reason for contacting a specialist.
The early symptoms of melanoma are as follows:
- Bleeding formation.
- A burning sensation occurs.
- Growth of a flat mole upwards.
- Itching, ulceration of the formation.
- Mole softening.
- The presence of any other discharge at the location of the mole.
- Birthmark growth on the periphery.
- Puffiness of adjacent tissues.
- Discoloration of fabrics next to existing moles.
Late symptoms of melanoma
Symptoms that indicate the progression of the disease include:
- Damage to the skin with a violation of their integrity.
- Isolation of blood from education.
- Discharge of blood from other pigmented areas on the skin.
- The appearance of painful sensations.
Symptoms suggestive of metastases
Metastasis means that tumor cells have entered the bloodstream and spread to other organs:
- The appearance of a chronic cough.
- The appearance of a dense area under the skin.
- Acquisition of a gray tint by the skin.
- Headaches on a regular basis.
- Convulsions.
- Weight loss, even to the point of exhaustion.
- Swollen lymph nodes.
The following conditions require urgent medical attention:
- Discharge of blood from a mole, or from the pigmented area;
- Asymmetry of a mole;
- Change in the color of the nails, in the absence of their prior injury;
- Darkening of the skin area, not caused by sunburn;
- The appearance of areas of skin with uneven edges;
- The appearance of multi-colored moles, or the spread of pigmentation from the mole to nearby tissues;
- The diameter of a mole or birthmark is more than 0.6 cm
Melanoma stages

The modern classification distinguishes several stages of melanoma, depending on its thickness, the presence of ulceration and the rate of division of diseased cells.
Tumor thickness or Breslow thickness is an indicator that is measured in millimeters. Melanoma is measured from the top layer of the skin to the deepest point of growth. The thinner the tumor, the higher the chance of recovery. It is the thickness of Breslow that is taken as a basis when making a prognosis for survival and to assess the effect of the therapy.
First and second stage
Melanoma is limited, metastases are absent, the effectiveness of timely treatment is assessed as high, the risk of recurrence is minimal.
It is customary to distinguish between the following tumors, depending on their thickness:
- The tumor is in situ or "in situ". This is a zero stage, the tumor has not penetrated into the deep layers of the epidermis.
- A tumor less than 0.1 cm is a thin melanoma. This is the first stage of the disease.
- The tumor is 0.1 cm-0.4 cm. This thickness indicates the transition of melanoma to the second stage.
- A tumor larger than 0.4 cm is a thick melanoma.
If there are small ulcerations on the formation, then this indicates a higher severity of the disease. For the prognosis, an indicator such as the rate of division of melanoma cells matters. If at least a single case of cancer cell division is recorded by 1 mm squared, this indicates a higher risk of developing metastases and an early transition of the disease to a severe stage. In this case, aggressive treatment is necessary to save the patient's life. The first two stages are characterized by the absence of any subjective sensations, the tumor simply grows both in width and height.
The third stage of melanoma
With the transition of the disease to this stage, the thickness of Breslow ceases to matter. In this case, ulceration of the tumor comes to the fore.
Melanoma grows deeper and invades the lymph nodes and surrounding areas of the skin. The beginning of the third stage is evidenced by the exit of the tumor beyond the initial boundaries. To confirm the existing assumptions, a biopsy of the lymph nodes located in the immediate vicinity of the melanoma is performed. In addition, a biopsy is carried out in the presence of areas of ulceration on the tumor and with an increase of more than 0.1 cm. The third stage is characterized by painful sensations and other late symptoms.
Stage four melanoma
At this stage of the disease, the tumor metastasizes. Lungs, liver, bones, brain, digestive tract organs can be involved in the pathological process. The prognosis for recovery is unfavorable, the survival rate does not exceed 10%. As for the symptoms, they depend on which organ is involved in the pathological process, except for the skin.
What does melanoma look like?

Melanoma diagnostics
The diagnosis of melanoma is difficult and can be challenging even for qualified dermatologists with experience. The symptoms of the disease do not always manifest themselves clearly, therefore, the patients themselves should be especially attentive to any formations that appear on their skin and notify the doctor in a timely manner. Particular vigilance should be exercised by those people whose relatives have suffered a similar pathology. After examining the suspicious lesion, the doctor may send the patient for a skin biopsy and for a lymph node biopsy. An accurate diagnosis can be made only on the basis of histological data.
The sooner the disease is detected, the more chances that the patient's life can be saved. Doctors strongly recommend that you examine your own skin every month for any skin changes. At the same time, a person does not need special devices, a sufficiently large and small mirror, a bright light source, a pair of chairs and a hair dryer.
- To assess the condition of the scalp, it is convenient to use a hairdryer. The head and face are viewed using a pair of mirrors.
- It is important to assess the condition of the nails and hands, examine the shoulder blades, armpits, and shoulders.
- Women should definitely pay attention to the skin under the breasts.
- Next, you should examine the neck, trunk and mammary glands.
- Don't forget about your legs, including your knees and feet.
- A small mirror will allow you to assess the condition of the genital skin.
If any formations were found, then you need to compare them with the photographs presented above.
Disease prognosis
As for the prognosis for recovery, it directly depends on the stage of development of the disease. If melanoma is detected early, the prognosis is good.
There is a risk of recurrence of the disease when the melanoma grows deeply. If the depth is more than 0.4 cm, or there is already inflammation in the lymph node, then the risk of metastases penetrating into other organs is extremely high. The presence of secondary foci of infection makes the therapeutic regimen ineffective.
When a person has already been diagnosed with melanoma, and he has successfully undergone treatment, it is extremely important for him to conduct an independent examination, since the risk of a relapse of the disease in this case is extremely high. This can happen even several years after recovery.
At the first stage, recovery is quite likely, in addition, patients can get rid of melanoma at the second stage of the development of the disease.
If we consider the statistics in percentage terms, then the five-year survival rate of patients is as follows:
- First stage therapy - 95% of patients with 5-year survival, 88% of patients with 10-year survival.
- Second stage therapy - 79% of patients with 5-year survival, 64% of patients with 10-year survival.
- Stage III therapy - 29% -69% (data vary) of patients with 5-year survival, 15% of patients with 10-year survival.
- Stage 4 therapy - 7% -19% of patients with 5-year survival. As for the ten-year survival rate of patients with stage 4 melanoma, there are no such data.
If the tumor is thicker, if metastases are found in nearby tissues, if melanoma is prone to ulceration, then the likelihood of recurrence of the disease is high. It is important to understand that secondary melanoma can appear both next to the past pathological formation, and far from it.
Although melanoma is a very formidable disease, almost always its early diagnosis and timely treatment leads to a complete recovery of the patient and guarantees long-term survival.

The author of the article: Bykov Evgeny Pavlovich | Oncologist, surgeon
Education: graduated from residency at the Russian Scientific Oncological Center. N. N. Blokhin "and received a diploma in the specialty" Oncologist"
Recommended:
Pancreatic Cancer - Signs And Symptoms, Stages And Degrees, Pancreatic Cancer Treatment

Pancreatic cancer causes, symptoms and treatmentWhat is Pancreatic Cancer?Pancreatic cancer is one of the malignant neoplasms of the pancreas, which is a tumor growth of atypical cells of the glandular or squamous epithelium lining the acinar elements or ductal system
HIV Infection In Men And Women - Signs, Symptoms, Stages And Routes Of Infection

HIV infection: symptoms, stages and routes of infectionHIV is an abbreviation for Human Immunodeficiency Virus. The virus attacks the immune system of the human body, introducing HIV infection into it. As it develops, this infection manifests itself in various symptoms, combined in the "acquired immunodeficiency syndrome" or AIDS
Melanoma - Eye Melanoma, Symptoms And Treatment

Symptoms and treatment of ocular melanomaMelanoma (melanoblastoma) refers to malignant tumors that form in the place of pigment cells (melanocytes) producing melanin. The most likely place of localization of pathology is the skin, less often mucous membranes are affected (retina, mouth, vagina, anus)
Skin Melanoma - Mole Melanoma, Pigmented Melanoma, Facial Melanoma

Melanoma of a mole, pigmented, on the faceDefinition of melanomaMelanoma is a very dangerous disease that is much easier to prevent than cure. Melanoma of the skin is a malignant tumor that occurs at any age. Such a common type of disease, as a rule, arises from special melanocytes of normal skin, as well as from pigmented nevi
Diagnosis Of HIV Infection - 3 Stages Of Diagnosis

Diagnosis of HIV infectionHIV testing is used for early diagnosis. Methods for diagnosing infection are constantly being improved, since the main symptoms of the disease do not appear immediately, disguising themselves as other pathologies