2024 Author: Josephine Shorter | [email protected]. Last modified: 2024-01-07 17:49
Diuretics (diuretics)

Diuretics are chemical compounds that ensure the reabsorption of water and sodium ions from body tissues. Medicines from this pharmacological group increase the volume of fluid excreted from the urinary system.
The mechanism of action of drugs is heterogeneous - some of them act by affecting renal hemodynamics, some - at the level of the tubules.
It is important to choose the right diuretics, because the predicted outcome of treatment depends on this.
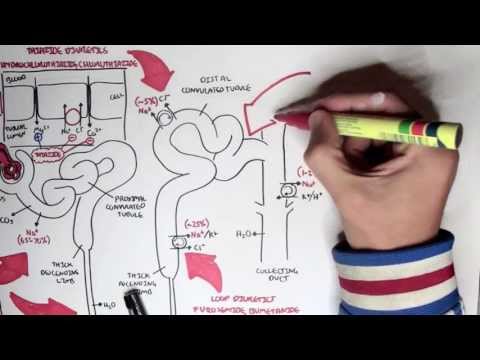
In the treatment of many diseases, loop diuretics are actively used, acting at the level of the ascending part of the Gentle loop. An example of loop diuretics is Furosemide, which has been traditionally used by physicians and urologists for many years. Osmotic diuretics and carbonic anhydrase inhibitors are less actively used.
In quinazolones and chlorobenzamides, the mechanism and strength of action are close to loop diuretics. They act gently, but with a prolonged result that lasts for a day.
Potassium-sparing diuretics (pterides and carboxamides) act for a long time, are not contraindicated in patients with chronic renal failure. Diuretics of this group do not have a negative effect on glomerular filtration.
The main classes of diuretics are:

Content:
- Diuretics in foods
- Loop diuretics
- Thiazide diuretics and their close relatives
- Potassium-sparing diuretics
- When should or should not you use diuretics?
- When does a doctor prescribe a diuretic?
- Adverse effects of diuretics
- Contraindications for taking diuretics
- Dangerous combinations
Diuretics in foods

For those who need diuretics, there is the option of using natural diuretics. This is the use of diuretic herbal preparations, products that can remove excess fluid from the body, the use of a diet with a minimum amount of table salt in the diet.
Such measures are applicable to the treatment of practically healthy people, whose edema is associated with excessive consumption of salty foods, overwork, and a violation of the diet.
Herbs with a diuretic effect:
- Pharmaceutical camomile,
- Chicory,
- Birch buds and leaves
- Dill greens,
- Horsetail,
- Bird Highlander,
- Juniper,
- Lingonberry leaf,
- Burdock leaves and roots
- Rosehip roots and berries,
- Bearberry,
- Flax seed;
- Parsley root.
These plants can be used alone or as part of herbal preparations.
The choice of diuretic plants depending on the sympathetic:

Diuretic products:
- Watermelon,
- Melon,
- A pineapple,
- Cucumbers,
- Cranberry,
- Dill, parsley, celery.
A product such as baked potatoes has a double effect: it is a source of potassium and has diuretic properties. For weight loss, they use a three-day diet based on it, during which they consume a kilogram of baked potatoes during the day, washed down with water. In 3 days, you can get rid of 2.5-3 kg of excess weight and puffiness.
Loop diuretics

Loop diuretics have the following properties:
- Acting quickly (within 15-30 minutes);
- The action of the drug lasts for 2-6 hours;
- With intravenous administration, hemodynamic parameters are changed: end diastolic pressure and end diastolic volume are reduced in case of left ventricular failure and pulmonary hypertension);
- Reduces the volume of extracellular fluid and the intensity of shortness of breath.
Loop diuretics, due to their advantages, are often used in the emergency complex relief of symptoms of cardiovascular and renal failure.
Video about the effect of various diuretics on the human body:
Representatives of loop diuretics:
-
Furosemide (Lasix). The drug for speed is taken on an empty stomach, it works after 30-50 minutes, with intravenous administration - after 5 minutes. When administered orally after 4-6 hours, most of the active substance is excreted along with the urine, with intravenous administration - after 2 hours.
- Torasemide. Has a longer duration of action, removes less potassium than Furosemide. In the treatment of heart and renal failure, Lasix is more effective.
- Bumetanide (Burineks, Yurineks). It is rapidly absorbed, after 30 minutes it has a diuretic effect, it is used for swelling of the face and limbs, with hypertension against the background of severe renal failure.
- Pyrethanides. Has a significant effect, much greater than that of Furosemide. It is used as an effective antihypertensive agent, calcium channel blocker, for edema, heart and kidney failure.
- Ethacrynic acid (Uregit). The diuretic effect is strongly pronounced, the effect lasts from 2 to 6 hours. Used for puffiness, has contraindications: anuria, oliguria, hepatic coma.
All representatives of diuretics in an increased volume remove potassium and other trace elements: magnesium, sodium, calcium, chlorine.
To compensate for the loss of valuable substances, Panagin, Asparkam, potassium orotate are simultaneously prescribed.
Thiazide diuretics and their close relatives

The drugs of this group are available in the form of tablets and are used in the complex treatment of edema and arterial hypertension. The mechanism of action of thiazide diuretics is to block the reverse transport of sodium and chlorine.
TD properties:
- Reduce the volume of blood plasma and extracellular fluid;
- Provide a drop in cardiac output and peripheral vascular resistance;
- Reduce hell.
If the patient does not respond to TD therapy, the doctor prescribes the simultaneous administration of ACE inhibitors, which help to cope with high blood pressure and edema in combination.
Why do hypertensive patients love them? TDs do not remove substances from the body that feed the heart muscle and ensure its normal functioning. In addition, thiazide diuretics have a period of diuretic effect several times longer than that of loop diuretics - from 18 hours versus 3-6 hours for PD.
Thiazide diuretics stimulate a mild diuretic effect that does not require frequent emptying of the bladder. All processes occur close to the physiological norm, which allows you to take TD on trips, at work.
To lower blood pressure, thiazide diuretics can be used in combination with other potassium-sparing diuretics and drugs with an antihypertensive effect. In some cases, it is enough to take minimal doses, the effect of the use of which will be noticeable after 3-4 weeks.
The use of thiazide diuretics reduces the likelihood of side effects:
- Hypokalemia - serum potassium deficiency;
- Hyperlipoproteinemia - an increase in the level of fatty amino acids that contribute to the development of atherosclerosis;
- Heart rhythm disturbance due to loss of minerals.
"Close relatives" of TD are non-thiazide sulfanilamide diuretics, and drugs that occupy an intermediate position between loop and sulfanilamide diuretics (Xipamide).
Diuretic tablets from the thiazide diuretic group:
- Hydrochlorothiazide (Esidrex, Hypothiazide). In terms of effectiveness and duration of action, it belongs to the middle stage diuretics, shows its properties after 1-2 hours, the effect lasts 12-18 hours. The drug does not disturb the acid-base balance and can be used for a long time. When taking it, it is required to enrich the diet with potassium, to reduce the daily intake of salt.
- Indapamide (Pamid, Indapafon, Arifon). A diuretic that combines a diuretic and hypotensive effect. Protects the heart and blood vessels, does not affect the functionality of the kidneys, does not violate the lipid balance.
- Chlorthalidone (Oxodolin, Hygroton). Sulfanilamide diuretic of medium strength has a long-term effect (up to 3 days), similar to the action of hypothiazide.
- Clopamide (Brinaldix). Pharmacodynamics and other properties are equivalent to Hypothiazide and Chlorthalidone.
Comparison of loop and thiazide diuretics:

Potassium-sparing diuretics

Diuretics of this pharmacological group have a mild but long-lasting effect that occurs some time after the start of treatment. Potassium-sparing diuretics do not work as quickly as loop or thiazide diuretics. For example, Triamteren relieves swelling only after 3 hours from taking the drug, although due to the mild effect, not all patients notice this.
Potassium-sparing diuretics act as an adjuvant in hypertension. Their main purpose is a diuretic effect in the treatment of puffiness. The combination of thiazide diuretics with the main substance of potassium-sparing diuretics (Triampur, Makzid, Diazid) works very harmoniously.
Typical representatives of KSD:
- Spironolactone (Veroshpiron, Aldactone). Has a prolonged effect, which appears from 3-5 days, and lasts 2-3 days after cancellation. The antihypertensive effect is manifested after 2 weeks from the beginning of the intake, therefore, with severe hypertension, other antihypertensive and diuretic drugs are prescribed simultaneously. Since Spironolactone is a drug from the group of steroids, it negatively affects the balance of hormones, among the side effects of gynecomastia, male-pattern hair growth.
- Triamteren (Daitek, Pteroferon). The action lasts 12-15 hours, occurs 2 hours after ingestion. The hypotensive effect is more pronounced than that of the previous drug. In elderly patients, it stimulates the deposition of calcium in the kidney tubules, which changes the natural color of urine to blue or blue.
- Amiloride (Midamor). A mild diuretic that stimulates the action of thiazide diuretics. In combination with hypothiazide, it is used in the treatment of hypertension and heart failure.
When should or should not you use diuretics?

You should not use diuretics to reduce excess weight, as they have the following properties:
- Diuretic drugs help you lose weight by removing water from your body. The lost pounds will come back very soon.
- The loss of fluid must be replenished, so after taking powerful diuretics, the person is very thirsty.
- Obesity cannot be eliminated with diuretics.
The use of diuretics against the background of diabetes mellitus requires special care. Diabetic foot syndrome is accompanied by leg edema, but the use of diuretics for systemic pathology requires many factors to be considered. Each case of edema of the lower extremities requires clarification of the cause of this condition (varicose veins, overwork, heart failure). In mild cases, the use of folk remedies will suffice.
With puffiness of the face, it is important to exclude kidney pathology. If not, eating foods with diuretic properties will help.
Edema during pregnancy occurs due to venous stasis, hormonal changes in the body, and an increase in the load on the body. It is dangerous if edema in the second half of pregnancy is the result of gestosis - late toxicosis of pregnancy. As prescribed by a doctor, thiazide diuretics are prescribed as an exception in the second and third trimester of pregnancy.
When does a doctor prescribe a diuretic?

List of indications for admission:
- Arterial hypertension, not complicated by renal failure. A decrease in systolic pressure occurs due to a decrease in blood volume in the vascular system. A sharp drop in pressure does not occur, its indicators decrease moderately, without the development of hypotension. The antihypertensive effect is achieved by increasing the potassium content and decreasing sodium. After 1-2 months, diastolic pressure is normalized while maintaining the volume of cardiac output. Diuretics are not addictive, do not affect potency and libido.
- Chronic circulatory failure on the background of edema and arterial hypertension. To correct this condition, strong diuretics of short and medium duration are used. Indications for emergency therapy: pulmonary edema, cerebral edema, barbiturate poisoning.
- Prevention of hypokalemia and secondary hyperaldosteronism against the background of hypertension and chronic renal failure.
- Diabetes insipidus.
- Glaucoma.
Adverse effects of diuretics
Micronutrient loss disorders

Diuretics remove from the body the ions of valuable chemical compounds involved in metabolism. An imbalance in electrolytes leads to side effects: arrhythmia, decreased blood pressure, impotence.
Cons of using diuretics:
- A sharp decrease in potassium levels;
- A decrease in the level of magnesium - manifests itself when taking loop diuretics, less - when taking thiazide diuretics, potassium-sparing diuretics are not completely removed;
- Decreased calcium levels - to a large extent excreted by loop diuretics (up to 30%), potassium-sparing diuretics accumulate calcium, leading to hypercalcemia;
- A decrease in sodium levels - noted with self-medication with diuretics, symptoms: weakness, nausea, drowsiness.
The consequence of exceeding the dosage of diuretic drugs can be mental disorders, coma.
Arrhythmia, metabolic disorders
Long-term use of thiazide diuretics against the background of arterial hypertension can lead to arrhythmias and sudden coronary death.
Factors provoking arrhythmia:
- Hypokalemia leading to myocardial instability;
- Left ventricular hypertrophy;
- Psycho-emotional stress;
Types of diuretics and typical side effects:

Other side effects of diuretics include:
- Decrease in the mass of the left ventricular myocardium up to 11% (Indalamid);
- An increase in the level of uric acid in the blood, the development of gout, chronic nephropathy (characteristic of patients with overweight);
- Persistent increase in glucose levels (hyperlipidemia) leading to diabetes mellitus;
- Violation of the lipid spectrum (hyperlipidemia), leading to an increase in the level of lipoproteins in the blood, normalizes after drug withdrawal;
- Violation of acid-base balance, leading to metabolic alkalosis;
- Development of hyperkalemia and metabolic acidosis with the use of potassium-sparing diuretics.
Contraindications for taking diuretics

General and relative contraindications:
- First trimester pregnancy.
- Diabetes mellitus (for hydrochlorothiazide).
- Renal and hepatic impairment (except for Amiloride).
- Anemia and hypervolemia (for Furosemide, Uregit).
- Hyperkalemia, incomplete atrioventricular block (for potassium-sparing diuretics).
- Simultaneous administration of several diuretics that do not excrete potassium.
Dangerous combinations

It is important to consider drug compatibility to prevent unpredictable side effects of such a compound.
- When potassium-sparing diuretics are combined with digitalis derivatives, the risk of arrhythmia increases.
- When Triamterene and Spironolactone are combined with Digoxin, the heart rhythm is disturbed.
- Potassium-sparing diuretics are not combined with a diet rich in potassium, with drugs containing this element.
- Drugs that increase blood glucose levels increase the hyperglycemic effect of diuretics.
- Aminoglycosides (Gentomycin, Kanamycin, Streptomycin) in combination with loop diuretics lead to damage to the kidneys, vestibular apparatus, and hearing organs.
- Taking diuretics against the background of NSAIDs reduces the diuretic effect.
When taking diuretics, it is important to consider the possible consequences and contraindications.

Author of the article: Lebedev Andrey Sergeevich | Urologist
Education: Diploma in the specialty "Andrology" received after completing residency at the Department of Endoscopic Urology of the Russian Medical Academy of Postgraduate Education in the urological center of the Central Clinical Hospital No. 1 of JSC Russian Railways (2007). Postgraduate studies were completed here by 2010.
Recommended:
Angina Pectoris - What Is It? What Do We Have To Do? List Of Medicines

Angina pectoris: symptoms and treatmentAngina is a sharp, severe pain in some parts of the heart that occurs due to a lack of blood supply. This is because the vessels become clogged or narrowed.When angina pectoris makes itself felt, the patient feels a compressive pain in the chest area, which can be given to the jaw, arm, neck, shoulder
Foot Fungus - Symptoms, Effective Treatment Of Foot Fungus, A List Of Inexpensive Drugs

Causes, symptoms and treatment of foot fungusWhat is foot fungus?Foot fungus is a mycotic lesion of the skin of the interdigital spaces with the possibility of including toenails in the pathological process (onychomycosis) and further spreading to other parts of the human body
Multiple Sclerosis - The First Signs, Symptoms And Causes. List Of Medicines

Multiple sclerosis causes, symptoms and medications listMultiple sclerosis is a neurological pathology characterized by a progressive course with multiple lesions in the central nervous system and fewer lesions in the peripheral nervous system
Fiber: Which Foods Contain It? TOP List

Fiber: benefits, types + TOP productsWhat is fiber?In some parts of plants, special fibers are formed - fiber. The peculiarity of these fibers is that they are not susceptible to the action of enzymes secreted by the upper parts of the digestive tract
Antiplatelet Agents - Mechanism Of Action, List Of Drugs

Antiplatelet agents: a list of drugsAntiplatelet agents are a group of medicines that are designed to suppress the process of thrombus formation by inhibiting the adhesion of platelets to each other. In addition, taking antiplatelet agents prevents platelets from adhering to the vascular wall