2024 Author: Josephine Shorter | [email protected]. Last modified: 2024-01-07 17:49
Cerebral aneurysm
Aneurysm of cerebral vessels - what is it?

A cerebral aneurysm is an expansion of one or more cerebral vessels. This condition is always associated with high risks of death or disability of the patient if the aneurysm ruptures. In fact, an aneurysm is a bulging of the vascular wall that occurs in a particular area of the brain. Aneurysm can be congenital, or it can develop during life. At the same time, it damages the integrity of blood vessels and often leads to cerebral hemorrhages. It is they who carry the main threat not only to health, but also to human life. As a rule, aneurysm rupture occurs in people aged 40-60 years.
Since the diagnosis of cerebral aneurysm is associated with certain difficulties, it is rather difficult to determine the real degree of its prevalence among the population. However, the statistics are that for 100,000 people, 10-12 of them have aneurysm. Posthumous autopsies show that aneurysms that did not provoke a cerebral artery rupture were not diagnosed in 50% during a person's life. They are discovered by chance, since they do not give any symptoms.
Nevertheless, the leading threat of aneurysm was and remains a rupture of the vessel with cerebral hemorrhage. This situation requires urgent medical attention, which is not always effective. The harsh statistics is that against the background of subarachnoid bleeding, 10% of patients die almost instantly, even before doctors have the opportunity to provide them with first aid. Another 25% of people die on the first day, and up to 49% die within the first three months after the incident cerebral hemorrhage. Summing up the sad conclusion, we can say that the death rate against the background of a ruptured cerebral aneurysm is equal to 69%. Moreover, the death of patients happens more often in the first hours or days after a brain catastrophe.
Despite the high development of medical science, the only method of treating cerebral aneurysm is surgery. However, even it does not provide 100% protection against death. However, the risk of death of a person from a sudden rupture of an aneurysm in comparison with the risk of death during or after surgery remains 2-2.5 times higher.
As for the countries where cerebral aneurysm is most common, the leaders in this regard are Japan and Finland. If we refer to gender, then men suffer from this pathology 1.5 times less often. In women, giant protrusions are three times more likely to be found. Aneurysms are very dangerous for women in position.
Content:
- What leads to the formation of a cerebral aneurysm?
- What can be an aneurysm of cerebral vessels?
- How does cerebral aneurysm manifest?
- Possible consequences of a cerebral aneurysm
- Consequences of ruptured aneurysm
- Diagnostics
- Examination of a patient with suspected aneurysm
- Treatment of cerebral aneurysm
- Possible consequences of surgical treatment
- About the prognosis of the disease
- Preventive actions
- Rehabilitation of patients
- Disability and aneurysm
What leads to the formation of a cerebral aneurysm?

The leading causal formation of aneurysm can be called a violation of the structure of any layer of the vascular wall, of which there are three: intima, media and adventitia. If these three membranes are not damaged, then an aneurysm will never form in them.
The reasons provoking its formation include:
- Postponed inflammation of the membranes of the brain - meningitis. Against the background of the disease itself, it can be quite difficult to identify the symptoms of an aneurysm, since the person's condition remains serious. After the meningitis is treated, defects may remain on the walls of the vessels of the brain, which will further lead to the formation of an aneurysm.
- Head injuries that provoke the dissection of the vascular walls.
- The presence of a systemic disease. The danger is bacterial endocarditis, untreated syphilis and other infections that reach the blood vessels of the brain with blood flow and damage them from the inside.
- Some diseases of a congenital nature (Marfan syndrome, tuberculous sclerosis, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, systemic lupus erythematosus, congenital polycystic kidney disease and some others).
- Hypertension.
- Autoimmune diseases that cause damage to the arteries.
- Atherosclerosis.
- Other reasons, including: cerebral amyloid angiopathy, malignant tumors that will not necessarily be localized in the brain.
Aneurysm of cerebral vessels is not inherited, however, it can occur against the background of diseases to which a person has a predisposition. Such diseases, for example, include hypertension, atherosclerosis, some immune and genetic pathologies.
What can be an aneurysm of cerebral vessels?

There are several types of classification of cerebral aneurysms, each of which has its own classification criterion. Having determined what kind of aneurysm the patient has, you can choose an effective treatment and make the most accurate prognosis.
-
Types of vascular aneurysms depending on their shape
- The aneurysm is saccular. This aneurysm occurs more often than others, if we consider exclusively the vessels of the brain.
- Fusiform aneurysm. It most often forms on the aorta, but rarely develops in the brain. The aneurysm has a cylindrical shape and causes a fairly uniform expansion of the vascular wall.
-
Exfoliating aneurysm. It has an oblong shape and is located between the layers that make up the vessel wall. Most often, such an aneurysm also occurs on the aorta, which is explained by the mechanism of its formation. It is formed when there is a defect in the intima, where blood gradually begins to enter. This leads to wall delamination and cavity formation. In the vessels of the brain, the blood pressure is not as high as in the aorta, so this type of aneurysm is rarely found here.
-
Types of vascular aneurysms depending on their size. The smaller the aneurysm, the more difficult it is to detect it during diagnostic procedures. In addition, these aneurysms are not symptomatic. Large aneurysms, in turn, put pressure on structures in the brain and cause symptoms. Do not assume that a small aneurysm is not dangerous, as they all grow over time. How quickly the aneurysm will grow in size is unknown.
- Large aneurysms are those larger than 25 mm.
- Aneurysms are medium - less than 25 mm in size.
- Small aneurysms are those whose diameter does not exceed 11 mm.
-
Types of vascular aneurysms depending on their location. This criterion largely determines the symptoms of the disease, since each segment of the brain is responsible for certain functions. So, a person may suffer to a greater extent hearing, speech, vision, coordination, breathing, heart function, etc. The names of the types of aneurysm in this case comes from the vessel on which it is located. In this regard, there are:
- Basilar artery aneurysms (occurs in 4% of all patients).
- Aneurysms of the posterior (26%), middle (25%) or anterior (45%) cerebral artery.
- Aneurysms of the lower and upper cerebellar arteries.
- Depending on when the aneurysm was formed, congenital and acquired defects are distinguished. Acquired aneurysms are more susceptible to rupture, which is explained by the high rate of their growth. Therefore, at the time of diagnosis, it is highly desirable to determine the timing of the bulge formation. For example, some aneurysms form in just a few days and rupture quickly. Other aneurysms, on the other hand, can exist for years and not give themselves away.
- Depending on the number of aneurysms, multiple and single formations are distinguished. Most often, a single protrusion is found in the brain - in 85% of cases. Risk factors for the formation of multiple aneurysms are serious brain injuries or surgical intervention on its structures (we are talking about global operations), as well as congenital diseases that impair the quality of connective tissue. Naturally, the more formations a person has, the worse the prognosis.
What is a saccular aneurysm?

The reasons for the formation of a saccular aneurysm are most often reduced to a point damage to a vessel, or rather, one of its layers. As a result, the vessel wall begins to gradually bulge outward, which leads to the appearance of a sac, which is filled with blood. Its bottom is often wider in comparison with the opening through which blood flows.
In the presence of saccular aneurysm, there is a risk of developing the following disorders:
- Deterioration in the supply of individual sections of the artery with blood, due to its slower current.
- Turbulence of blood during its movement through a vessel with an aneurysm.
- The presence of turbulence increases the risk of blood clots forming.
- The threat of rupture of the vessel wall increases, as it turns out to be too stretched.
- The brain can be damaged due to compression of its tissues by an aneurysm, which increases in size.
Still saccular aneurysms rupture more often and provoke the formation of blood clots when compared with other types of aneurysms.
What is a false aneurysm?
Pseudo-aneurysms are not widespread, however, they can occur. The defect is not a protrusion of the vessel, but its damage in the form of a rupture. Blood through the existing damage in the vessel wall flows out of its limits and begins to accumulate nearby, forming a hematoma. When the damage is not epithelialized, and the leaked blood itself does not spread, then a cavity is formed in the brain tissues, connected to the vessel. Such an aneurysm leads to disruption of blood flow, but at the same time it is not limited by the vascular wall. Therefore, doctors prefer to call such formations pulsating hematomas.
At the same time, a person remains at risk of developing massive bleeding in the brain tissue, because the damaged vessel wall remains disturbed. As for the signs of a false aneurysm, it can manifest itself as a true aneurysm or have symptoms of a hemorrhagic stroke. Making a differential diagnosis is very difficult, especially in the early stages of hematoma formation.
What is a congenital aneurysm?

If he talks about congenital aneurysms, then they mean those that a person had at the time of his birth. They began to form during the intrauterine life of the fetus and after birth do not disappear anywhere.
The following reasons can lead to their formation:
- Diseases transferred by a pregnant woman (viral infections are dangerous in this regard).
- The presence of a genetic disease that has a damaging effect on connective tissue.
- Intoxication of a woman's body during gestation.
- The presence of chronic diseases in a pregnant woman.
- Exposure to radioactive radiation on a pregnant woman.
Congenital aneurysms are most often found in those children whose mothers have undergone any harmful influence on the body from the outside. It is possible that the child will be born with other malformations, which happens very often.
It is rather difficult to make a single prognosis for each child with cerebral aneurysm. However, if the aneurysms are not false and the child has no other developmental defects, then the prognosis can be considered favorable, since the risk of a congenital aneurysm rupture is not great (their walls are thick enough). Nevertheless, a child should be registered with a pediatric neuropathologist from birth, since the presence of such an education in the brain can affect its development. If we consider the most severe cases, then aneurysms of a congenital nature are very large and sometimes incompatible with the life of the fetus.
How does cerebral aneurysm manifest?

For a long period of time, an aneurysm of the cerebral vessels may not give itself out. The protrusions rarely reach large sizes and are formed on small arteries (in the brain, all vessels are small). Therefore, the weak pressure that the aneurysm exerts on the brain tissue is often not enough for a person to show any symptoms of the disease.
However, sometimes the course of the disease can be quite severe, which occurs in the following situations:
- The aneurysm is large and presses heavily on areas of the brain;
- The aneurysm is located in the place of the brain that is responsible for extremely important functions;
- The aneurysm ruptures due to increased physical exertion on the body, against the background of stress, etc.;
- Against the background of hypertension and other chronic diseases, aneurysm can give more pronounced symptoms;
- Arteriovenous anastomosis aggravates the course of the disease.
Symptoms indicating the presence of an aneurysm include the following:
- Headaches that occur at different intervals and have different intensities.
- Insomnia, or increased drowsiness.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Meningeal symptoms that can occur with aneurysms located in close proximity to the membranes of the brain.
- Convulsions.
- Deterioration of skin sensitivity, impaired vision, coordination, hearing. The specific manifestations of the disease primarily depend on where the aneurysm is located.
- Disorders in the work of the cranial nerves responsible for the movement of small muscles. The patient may experience facial asymmetry, hoarseness, drooping eyelids, etc.
Possible consequences of a cerebral aneurysm

Complications of cerebral aneurysm can include almost any symptoms of this pathology, since they all lead to one or another disorder. So, it is difficult not to call the loss of vision or hearing a complication, which is provoked by compression of the nervous tissue by dilated blood vessels.
In addition, an aneurysm can cause other dangerous consequences for human health, for example, which occur when it ruptures. Other complications occur somewhat less frequently, but they carry no less threat.
Complications that can occur against the background of the presence of a cerebral aneurysm:
- Coma. If an aneurysm forms in those parts of the brain that are responsible for the vital functions of a person, then he may fall into a coma. The duration of a coma can be different, and often life-long. Moreover, despite high-quality and timely medical care, many patients never come out of this life-threatening condition.
- Thrombus formation. In the cavity of the formed aneurysm, a slowdown and disruption of blood flow may occur, which leads to the appearance of a blood clot. Most often, such a complication develops against the background of the presence of a large aneurysm. The location of the thrombus may vary: sometimes it occurs in the cavity of the aneurysm itself, and sometimes it breaks off and blocks the blood flow in smaller vessels. The more massive the thrombus, the more serious the threat to a person's life, since with this development of events he always suffers an ischemic stroke. However, with the provision of timely medical care, the patient's life can be saved. Often, a blood clot can be dissolved with the help of drugs.
- Formation of AVM. AVM is an arteriovenous malformation, which is essentially a defect in the vascular wall. This violation leads to partial adhesion of the vein and artery. The pressure in the artery cavity begins to drop, and some of the blood flows into the vein. This leads to an increase in pressure in the vein, and those areas of the brain that were fed from the artery begin to experience hypoxia. AVM is indicated by the same signs that occur against the background of ischemic stroke. Sometimes the symptoms of AVM are difficult to distinguish from the symptoms of a cerebral aneurysm. The larger the aneurysm, the more the vessel stretches, which means the higher the risk of AVM formation. With the development of this complication, surgical intervention is required.
Due to the fact that an aneurysm is capable of provoking serious complications that threaten a person's life, doctors, upon detection, insist on an operation. Moreover, the need for surgery is also due to the severity of the symptoms of the aneurysm itself.
Consequences of ruptured aneurysm

There are certain factors that can lead to the fact that a ruptured cerebral aneurysm is more likely to occur, among these:
- Experienced stressful situation;
- Excessive physical stress on the body;
- Hypertension or surges in blood pressure;
- Drinking alcoholic beverages;
- Infectious diseases occurring against a background of high body temperature.
After a ruptured aneurysm in a person, symptoms begin to increase sharply, which in general is not characteristic of this disease. The patient's condition deteriorates sharply and requires immediate medical attention. Signs that may indicate a ruptured aneurysm are:
- Very acute onset of the disease.
- Severe headache that comes on suddenly. Some patients report sensations as if they were suddenly hit on the head. In the future, confusion, loss of consciousness and even coma are very often observed.
- A person's breathing quickens. The number of breaths and exhalations per minute can reach twenty.
- The heart begins to beat more often, tachycardia develops. Then it goes into bradycardia when the number of heart beats per minute does not exceed 60.
- In 10-20% of cases, the patient has seizures of many muscle groups.
In more than 25% of patients, a ruptured aneurysm is masked as other brain catastrophes.
To understand that a misfortune has happened to a person and not to delay calling an ambulance, you need to know the main signs indicating a ruptured cerebral aneurysm, including:
- Violent headaches;
- Feeling that blood rushes to the face;
- Deterioration of vision, which can be expressed in double vision in the eyes, in the feeling that the environment is stained red;
- Problems with the pronunciation of words and sounds;
- A feeling of buzzing in the ears that gets worse;
- The appearance of painful sensations in the eye socket, or in the face;
- Frequent muscle contractions in the legs and arms that the person is unable to control.
Often, these signs do not allow for a 100% correct diagnosis. Nevertheless, it can be understood from them that a person needs urgent medical attention.
A ruptured cerebral aneurysm is an extremely serious condition, and, what is most sad, it is not rare. Even with emergency hospitalization, the number of deaths remains high. In many ways, the prognosis depends on where exactly the gap occurred in the brain. It is possible that a person who survived after such a brain disaster will be able to restore speech, hearing, and movement. However, they can be lost or damaged permanently.
First aid rules for a person with a ruptured aneurysm:
- The person must be laid in such a way that his head is on a dais. This will reduce the likelihood of cerebral edema.
- All items of clothing that compress the airways should be removed (scarves, ties, neckerchiefs, etc.). If a person is in the room, it is necessary to provide a supply of fresh air.
- When the victim loses consciousness, the airway should be checked. The head must be turned to the side so that in case of vomiting, the masses do not enter the respiratory tract.
- Cold should be applied to the head, which will reduce the risk of cerebral edema and reduce the intensity of intracerebral bleeding.
- If possible, the patient should measure blood pressure and pulse.
Naturally, one should not expect a miraculous effect from such events and they are not able to exclude a lethal outcome. Nevertheless, it is imperative to try to fight for a person's life before the arrival of an ambulance team.
Diagnostics

It can be quite problematic to identify an aneurysm of the cerebral vessels, since it often does not give any symptoms. Almost any specialist can suspect this pathology, which a sick person has to go through a lot. This is not surprising, because headaches can be caused by hypertension, body intoxication and many other disorders. Moreover, even such a common symptom as headache does not always occur in people with an aneurysm.
The doctor must necessarily suspect the presence of any pathology of the central nervous system if the patient makes the following complaints or has symptoms such as:
- Deterioration of visual, olfactory and / or auditory function;
- The presence of seizures;
- Loss of skin sensitivity;
- Paralysis;
- Coordination disorder;
- The appearance of hallucinations;
- Incorrect pronunciation of words or their spelling, etc.
Nevertheless, doctors are armed with a number of techniques that allow timely detection of aneurysm of the cerebral vessels, but it is necessary to begin the examination with an examination of the patient who applied for an appointment.
Examination of a patient with suspected aneurysm

Naturally, a routine examination will not reveal and diagnose "cerebral aneurysm".
Nevertheless, the doctor is able to suspect this pathology and send the patient for a more thorough examination:
- Palpation allows you to assess the condition of the skin, as well as to suspect the presence of systemic diseases of the connective tissue. It is known that they are often the cause of aneurysm formation.
- With percussion, the doctor will not be able to identify an aneurysm, but this method makes it possible to detect other diseases that may accompany a defect in the cerebral vessels.
- Listening to the noises of the body allows you to detect pathological sounds that occur in the region of the heart, aorta, carotid artery. Taken together, these diagnostic criteria can lead the doctor to the idea of the need for a thorough examination of the vessels of the brain.
- Determination of the blood pressure level. It is known that an increased level of blood pressure is a factor predisposing to the development of aneurysm. In the event that the patient already knows his diagnosis, he must measure the pressure every day. Often, it is this manipulation that allows you to prevent or timely detect an aneurysm rupture.
- Neurological examination. During it, the doctor assesses the state of the patient's reflexes (skin and muscle-tendon reflexes), tries to detect pathological reflexes. In parallel, the doctor assesses the ability of a person to perform certain movements, the presence or absence of skin sensitivity. It is possible that the doctor will conduct an examination for the detection of meningeal symptoms.
The data obtained during the examination cannot serve as a basis for making an accurate diagnosis. It is important to differentiate it from a brain tumor, from a transient ischemic attack, from arteriovenous malformation, since all these pathological conditions give the same symptomatology.
Tomography as a method for diagnosing aneurysm. CT and MRI can be called the leading methods for detecting this defect in the cerebral vessels. However, they have some limitations. Thus, computed tomography is not prescribed for pregnant women, young children, patients with blood diseases and cancer. For a healthy adult, the dose of radiation that he receives during a CT scan is not dangerous.
As for MRI, this study is safe in terms of radiation exposure, but it is not indicated for all patients. For example, it is not performed if there is a metal-based implant or an electronic prosthesis in the human body. Also, MRI is contraindicated in patients with a pacemaker.
After conducting a computed or magnetic resonance imaging, the doctor will be able to obtain the following information about the cerebral aneurysm, if any:
- Its localization;
- Its size;
- The presence of a blood clot;
- Information on the number of aneurysms;
- Information about the state of the brain tissues surrounding the aneurysm and about the blood flow rate.
X-ray examination. Although the accuracy of angiography (X-ray examination with the introduction of a contrast agent into the vessels) is slightly lower than that of CT and MRI, in most cases it allows visualizing the existing bulging of the vascular wall. The most informative is angiography in the early development of the disease, which makes it possible to distinguish between a brain tumor and aneurysm of its vessels. However, CT and MRI are the most preferred methods for diagnosing this disease. Angiography is not recommended for pregnant women, children, patients with kidney disease.
EEG. An EEG does not allow for a diagnosis, but only provides information about the activity of certain parts of the brain. However, for an experienced doctor, it can be of value and push him into thinking about the need for more complex diagnostic measures, for example, MRI. In addition, EEG is absolutely safe for a person of any age and can be performed even for young children.
Treatment of cerebral aneurysm

The leading method of treating aneurysm is surgery. It will remove the formation itself and restore the integrity of the vessels.
Operation is the only effective method of treating cerebral aneurysm. If the size of the defect is more than 7 mm, then surgical treatment is mandatory. Emergency surgery is required for patients with a ruptured aneurysm. The following types of surgical intervention are possible:
Direct microsurgical intervention
This type of surgery is also called aneurysm clipping. It is it that is most often implemented in the practice of microsurgery. For the operation, craniotomy is required. The procedure itself lasts for many hours and carries high risks to the patient's health and life.
Stages of clipping:
- Craniotomy;
- Lancing of the meninges;
- Separation of the aneurysm from intact tissue
- Applying a clip to the body or neck of the aneurysm (this is necessary in order to remove it from the general bloodstream);
- Suturing.
To perform the operation, the doctor needs microsurgical equipment. In most cases, surgical intervention is completed successfully, however, no doctor is able to guarantee a favorable prognosis.
In addition to clipping, a direct microsurgical wrapping operation can be performed, when the damaged vessel is strengthened using a special gauze for this purpose, or a part of muscle tissue.
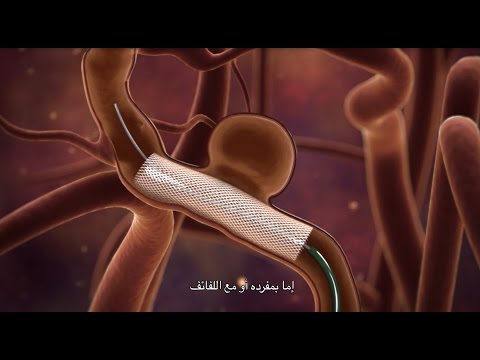
Endovascular surgery
These operations are high-tech and do not require craniotomy. The aneurysm can be accessed with a needle that reaches the brain via the carotid or femoral artery and closes the existing lumen with a balloon or micro-coil. They are fed through a needle through a catheter. As a result, the aneurysm is excluded from the general blood flow. The whole procedure is carried out under the control of a tomograph.
Another type of endovascular surgery is embolization of an aneurysm using a special substance that freezes and prevents it from filling with blood. This procedure is performed under the control of X-ray equipment with the introduction of a contrast agent.
If the hospital is equipped with equipment that allows endovascular surgery, then they should be given preference.
This is due to the following advantages of such techniques:
- Operations are low-traumatic;
- Most often, the patient does not need general anesthesia;
- Craniotomy is not required;
- The time of the patient's passage in the hospital is reduced;
- If the aneurysm is located in the deep tissues of the brain, then it will be possible to "neutralize" it only with the help of endovascular surgery.
- Combined operation.
This method involves a combination of a surgical technique with endovascular technology. For example, a vessel can be occluded with a balloon followed by clipping; in general, there can be many options.
It is worth understanding that any operation carries certain risks. This also applies to high-tech techniques.
Among the most common complications are:
- Vascular spasms;
- Rupture of the aneurysm with a balloon or spiral;
- Hypoxia;
- Embolism of the vessel with bloody clots;
- Rupture of the aneurysm during the operation;
- Death of a patient on the surgical table.
Video about endovascular embolization surgery, which uses natural access to the brain through arteries to diagnose and treat a cerebral aneurysm:
Medication correction
Medical correction should be aimed at preventing rupture of the aneurysm. For this, medicines such as:
- Nimodipine (30 mg / 4 times a day). The drug dilates blood vessels, relieves spasm from them, prevents surges in blood pressure.
- Captopril, Labetalol. The drugs lower the pressure by reducing the stress on the blood vessels.
- Phosphenytoin (IV, at the rate of 15-20 mg / kg). The drug eliminates the symptoms of the disease, contributes to the normal functioning of the nervous tissue.
- Morphine. They are used very rarely and for severe pain, exclusively in a hospital setting.
- Prochlorperazine (25 mg / day). The drug eliminates vomiting.
Possible consequences of surgical treatment

After craniotomy, the patient may suffer from tinnitus, severe headaches, loss of hearing and vision, impaired coordination, etc. Moreover, these consequences can be both temporary and permanent.
The main danger of endovascular aneurysm treatment is the formation of blood clots, as well as damage to the integrity of the vascular walls. However, most often such complications occur against the background of a medical error, or due to the occurrence of emergency situations during the operation.
To minimize the development of serious complications in the long-term postoperative period, it is necessary to adhere to the following recommendations:
- You cannot wash your hair after trepanation for periods of 14 days or more.
- Any sports involving the possibility of head injury should be prohibited.
- You should adhere to the dietary scheme of food, completely abandon the use of alcoholic beverages and spicy foods.
- Smoking of tobacco falls under the ban.
- For six months or more, after the operation, it is forbidden to visit steam rooms and a bath.
About the prognosis of the disease
If it is not possible to perform the operation, then the prognosis will definitely be unfavorable. Although there is evidence of patients who lived a long and prosperous life with an aneurysm and died from other diseases. Single congenital aneurysms can disappear on their own over time, however, the risk of re-formation remains high.
The most favorable prognosis can be considered in the presence of a single formation, a small size, and also when an aneurysm is found in a young patient. The prognosis of the presence of concomitant diseases and the presence of congenital connective tissue pathology worsens. The overall postoperative mortality rate is 10-12%.
Preventive actions

- It is necessary to constantly monitor the level of blood pressure and blood cholesterol.
- All bad habits should be abandoned.
- Nutrition must be correct.
- Stressful situations should be avoided whenever possible.
- If the patient has already been diagnosed with an aneurysm, then physical activity is contraindicated for him, and he also needs to take medications prescribed by the doctor. This measure is temporary, and it must be observed until the operation to remove the aneurysm.
Rehabilitation of patients
If the patient has suffered a ruptured aneurysm and survived, or when he had an operation to remove it, he needs to undergo a rehabilitation course.
It includes three areas:
- Position treatment using special braces. This method of rehabilitation is essential for paralyzed patients. It is carried out in the early stages.
- Massage performed by rehabilitation specialists.
- Heat treatment. In this case, applications with clay and ozokerite are used.
It is possible to supplement the rehabilitation course with physiotherapeutic procedures, which are selected on an individual basis and largely depend on the patient's condition.
Disability and aneurysm
To assign a disability group, the patient will need to go through a commission. Typically, an aneurysm often results in patients having serious health problems. When assessing a person's ability to work, doctors take into account many factors, including: the effectiveness of surgical treatment, the patient's working conditions, the type of aneurysm, its location, etc. Depending on the condition of a particular patient, the first one can be assigned to him (a person needs constant outside help), the second (weak working capacity remains) or the third group of disability (a person is able to serve himself independently, he does not need outside care).

Author of the article: Sokov Andrey Vladimirovich | Neurologist
Education: In 2005 completed an internship at the IM Sechenov First Moscow State Medical University and received a diploma in Neurology. In 2009, completed postgraduate studies in the specialty "Nervous diseases".
Recommended:
Surgery To Remove A Herniated Disc Of The Spine - Indications, Consequences, Types Of Surgery

Herniated disc surgeryContent:Indications for the operationWays to remove an intervertebral herniaConsequences of the operationWhen and what can you do?RehabilitationAn operation to remove an intervertebral hernia is one or another type of surgical intervention aimed at correcting and restoring the displaced nucleus pulposus of the intervertebral disc in case of rupture of the annulus fibrosus
Aortic Aneurysm Of The Heart - What Is It? Dangers And Consequences

Aortic aneurysmAortic aneurysm of the heart - what is it?Aortic aneurysm of the heart is a pathological expansion of one of the sections of the largest artery in the human body. The reason for the development of pathology is the weakness of the arterial wall
Surgery To Remove Uterine Fibroids - Is Surgery Necessary? Complications And Consequences

Surgery to remove uterine fibroidsA uterine fibroid is a benign tumor that develops from the muscle tissue of the female reproductive organ. In some cases, it requires surgical intervention, since conservative methods do not have the desired effect
Surgery For Stomach Cancer: Prognosis. How Long Do People Live After Surgery For Stomach Cancer

Stomach cancer surgeryDoctors believe that the main reasons for the occurrence of stomach cancer are the effects of bacteria called Helicobacter, and vitamin B12 deficiency. From the causes of the disease, sharp inflammatory processes that atrophy the stomach are not excluded
Lung Surgery For Cancer: Where To Start. How Lung Cancer Progresses After Surgery

Lung surgery for cancerThe main principle of cancer treatment today is the removal of the tissues of the malignant neoplasm of the lung, as much as possible.The operation to remove lung cancer is an extremely important measure, because only in this way it is possible not only to neutralize the tumor itself, but also to prevent its negative effects on the organ