Toxocariasis in children

Toxocariasis in children is a zoonotic helminthiasis, which is manifested by damage to the internal organs and eyes by nematode larvae migrating through the body. The disease is provoked by the toxocara worm (Toxocara canis). The worms have an elongated body resembling a cylinder, pointed at both ends. Females can be up to 10 cm long, and males 6 cm.
Adults parasitize in the body of dogs, wolves, jackals and other canines, less often toxocars are found in the body of cats. Animals release eggs into the environment, which after a certain time become invasive, after which they somehow enter the body of a mammal and migrate through it, causing symptoms of the disease. According to the classification of helminthiases, toxocariasis refers to geohelminthiasis, since eggs with larvae are preparing for invasion in the soil.
Toxocariasis in children is manifested by many different symptoms that even experienced doctors are sometimes unable to make a diagnosis based on the clinical picture of the disease. The fact is that the larvae can penetrate almost any organ of the child, as they migrate through the blood vessels. Depending on which organ is affected, the symptoms of the disease differ.
Nevertheless, always with toxocariasis, children develop allergic reactions such as urticaria or bronchial asthma. In severe cases, Quincke's edema is observed.
Toxocariasis is widespread among children under 14 years of age living in rural areas. Children from 3 to 5 years old are in the high-risk area. The disease can last for years, and the parents will unsuccessfully treat the child for a variety of pathologies. Only adequate antiparasitic therapy will save children from many health problems.
Content:
- Causes of toxocariasis in children
- Symptoms of toxocariasis in children
- Diagnosis of toxocariasis in children
- Treatment of toxocariasis in children
Causes of toxocariasis in children

Most often dogs are the source of infestation. Puppies are of the greatest epidemiological significance in terms of transmission. The causative agent of toxocariasis in cats is very rare.
The appearance of the parasites strongly resembles human roundworms, since they belong to the same group of helminths. Both toxocaras and roundworms have a similar structure, a similar life cycle. However, the final owner of the roundworm is a man, and the toxocar is a dog. Therefore, the symptoms of the disease differ.
If parasites enter the human body, which is a random host for them, then they provoke severe damage to internal organs, since they are not able to exist normally in his body. The larvae cannot adequately complete their life cycle and turn into a sexually mature individual.
Toxocars enter the body of animals (cats and dogs) through the gastrointestinal tract, most often this occurs when eating other infected mammals, when eating feces with larvae, during intrauterine development of puppies (larvae are able to penetrate the placenta), or when puppies are breastfed by a sick mother. Under the influence of the gastric environment, the larvae are released from their membrane, penetrate through the blood into the liver, into the inferior vena cava, into the right atrium and into the lungs. Then they rise into the trachea, into the larynx, into the throat, are swallowed again with saliva, again enter the digestive tract, where they reach puberty. It is in the small intestine of cats and dogs that toxocars live, parasitize and multiply. Their eggs are excreted together with feces into the external environment and after a certain time become ready for invasion.
Infection of children with toxocariasis occurs as follows:
- The child swallows the eggs of the worm from the fur of the animal.
- The child eats foodstuffs seeded with Toxocar eggs (most often fruits, vegetables, berries, herbs).
- The child eats the soil (most often sand) with toxocar eggs. This mainly happens during games in the sandbox and is explained by the age characteristics of children.
- Cockroaches pose a particular danger in terms of the transmission of toxocariasis to humans. They eat the eggs of the worm and excrete them in people's homes, often contaminating their feces with viable eggs on human food. This can lead to human infection.
- Pigs, chickens, and lambs can act as reservoir animals for toxocar larvae. Therefore, a child can become infected by eating infected meat.
It is young children who most often become infected with toxocariasis, since they have poorly formed rules of personal hygiene. The peak of invasion occurs in the warm season, when human contacts with the ground become more frequent.
Once in the child's body, toxocara larvae penetrate into the systemic circulation and settle in a variety of organs. Since the human body is an unsuitable environment for toxocara, the larva is enveloped in a dense capsule and in this form it will be inactive for a long time. In a similar state, parasite larvae can exist for many years. At the same time, the child's immune system does not allow her to move on, constantly attacking a foreign organism. As a result, in the place where the parasite stopped, chronic inflammation occurs. If the immune system is weakened, the worm is activated and the disease worsens.
Symptoms of toxocariasis in children

Symptoms of toxocariasis in children under the age of 12 are most often pronounced, sometimes the disease takes on a severe course. At an older age, it is possible that the symptoms of the disease are erased, or there is a complete absence of complaints from the patient.
Symptoms of toxocariasis in children should be considered through the form of the disease, that is, depending on which organ is affected by the parasite:
-
Visceral toxocariasis in children with internal organ damage. Since the larvae of the worm move through the body through the veins, they most often settle in those organs that are well supplied with blood, but the blood flow in them is weak. Mostly these are the lungs, liver and brain.
Considering the defeat of the child's digestive organs (liver, biliary tract, pancreas, intestines) by toxocar larvae, the following symptoms can be distinguished:
- Pain in the right hypochondrium, in the abdomen, in the navel.
- Appetite disorders.
- Bloating.
- Bitterness in the mouth.
- Frequent change of diarrhea and constipation.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Loss of body weight, lag in physical development.
If toxocars affect the lungs, then the child develops characteristic broncho-pulmonary symptoms with dry cough, shortness of breath, difficulty breathing. The development of bronchial asthma is not excluded. There is evidence of the manifestation of pneumonia, which ended in death.
If the larvae settle on the heart valves, then this leads to the development of the patient's heart failure. The child's skin, lower and upper limbs, nasolabial triangle turn blue. Even at rest, shortness of breath and coughing occur. With the defeat of the right half of the heart, severe edema appears on the legs. This condition requires urgent hospitalization.
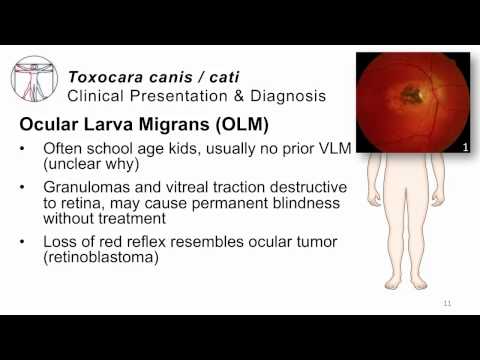
- Ocular toxocariasis in children. The organs of vision are rarely affected by toxocara larvae, this is manifested by loss of vision, conjunctival hyperemia, bulging of the eyeball, pain in the eye. One eye is most often affected.
- Cutaneous toxocariasis in children. If the larvae enter the dermis of the child, then this is manifested by severe itching, burning, a feeling of movement under the skin. In the place where the larva stops, as a rule, persistent inflammation occurs.
- Neurological toxocariasis in children. If the toxocara larva has penetrated into the meninges, then the disease manifests itself with characteristic neurological symptoms: behavioral disorders, loss of balance, headaches, sleep disturbances, dizziness, symptoms of focal brain damage (convulsions, paralysis, paresis, etc.).
Regardless of where the larva stopped, the immune system begins to attack it, which leads to the development of allergic reactions:

- Skin rash. Most often, it resembles mosquito bites and is shaped like a ring. The rash is intensely itchy and can occur almost anywhere on the body.
- Quincke's edema. This condition is characterized by swelling of the soft tissues in the neck. With a pronounced reaction, an attack of suffocation may occur, which, if proper assistance is not provided, will lead to the death of the child.
- Bronchial asthma. The child is constantly coughing. The cough is dry in nature, sputum is separated in small quantities. During an attack, strong wheezing and noisy breathing are heard.
The common symptoms of toxocariasis in children are:
- An increase in body temperature to 37-38 ° C and above, a feverish state.
- Intoxication of the body with weakness, headaches, loss of appetite.
- The enlargement of the lymph nodes in size, while they do not hurt and remain mobile.
- Pulmonary syndrome with persistent dry cough.
- Enlargement of the spleen and liver in size.
- Violation of the intestinal microflora.
- Frequent infections associated with the strength of the immune system.
Diagnosis of toxocariasis in children

Diagnosis of toxocariasis in children is very difficult, since it is very difficult to differentiate the symptoms of the disease from diseases of other organs. That is why such children have been treated unsuccessfully for a long time by gastroenterologists, pulmonologists and other narrow specialists. Pediatricians classify these children as frequently ill.
It is possible to suspect parasitic invasion by an increase in eosinophils in the blood (they are responsible for antiparasitic immunity) and an increase in total immunoglobulin E.
Sometimes toxocara larvae can be found in sputum during microscopic examination. Nevertheless, the most informative method for detecting this parasitic invasion is ELISA with the extrasecretory antigen of toxocara larvae.
Treatment of toxocariasis in children

Treatment of toxocariasis in children begins with the intake of anthelmintic drugs.
Most often, a child is prescribed one of the following medicines:
- Mintezol. The course of treatment can be 5-10 days.
- Vermox. The course of treatment can last from 14 to 28 days.
- Ditrazine citrate. The drug is taken for 2-4 weeks.
- Albendazole. The full course can last from 10 to 20 days.
In addition, the child needs to normalize the intestinal microflora. To do this, he is prescribed probiotics Linex, Bifiform, Bifidum forte, etc. In order to remove toxins from the intestines, adsorbents are prescribed, for example, Smecta or Enterol.
Symptomatic therapy is reduced to taking antipyretic drugs (Paracetamol, Ibuprofen). With severe abdominal pain, Papaverine may be prescribed. To eliminate allergic reactions, the child is prescribed antihistamines, including Zyrtek, Zodak, etc. Glucocorticosteroids are administered in case of severe disease with severe allergic reactions. The same applies to electrolyte solutions, which are administered intravenously in a hospital to reduce symptoms of intoxication.
It is imperative that children are prescribed hepatoprotectors to restore the functioning of the liver. If necessary, not only a parasitologist, pediatrician and infectious disease specialist, but also a neurologist, ophthalmologist, and surgeon are involved in the work.
When the symptoms of the disease are acute, then the placement of the child in a hospital is indicated.
In addition to taking medications, the child is transferred to a special diet, removing all products from the menu that could cause an allergic reaction. These are chocolate, citrus fruits, spices, smoked meats, etc.
When the child is discharged from the hospital, he is monitored by a pediatrician for another year, visiting him every 2 months. Depending on the severity of the disease, children are not vaccinated for 1-3 months. For the same period, they are given a medical withdrawal from physical education.
As a rule, the prognosis for toxocariasis in children is favorable, damage to the heart, brain and eyes is rare. However, it is very dangerous to delay with adequate therapy.

Author of the article: Danilova Tatyana Vyacheslavovna | Infectionist
Education: in 2008 received a diploma in the specialty "General Medicine (General Medicine)" at the Russian Research Medical University named after NI Pirogov. Immediately passed an internship and received a diploma of a therapist.