2024 Author: Josephine Shorter | [email protected]. Last modified: 2023-12-16 21:43
Atheroma of the ear in a child

Around the auricle there are a large number of sebaceous glands, so there is a high probability of atheroma formation in this area. It is a slowly growing subcutaneous fatty tumor that is benign in nature. According to medical statistics, atheroma occupies only about 0.2% of the total number of soft tissue neoplasms of the head. Most often, atheroma of the earlobe occurs, since there is a fatty layer, but the lobe does not have cartilage tissue.
ICD-10 atheroma code: L72.1. This is a trichodermal cyst.
Content:
- Factors for the development of atheroma near the auricle
- Signs of atheroma near the ear
- Pathogenesis of atheroma of the ear in children
- Behind the ear atheroma
- Atheroma on the earlobe
- Diagnostics of the atheroma behind the ear
- Treatment of atheroma on the earlobe
- Treatment behind the ear atheroma
Factors for the development of atheroma near the auricle

The main reason for the formation of atheroma is a blockage of the excretory duct of the sebaceous gland. This condition is caused by hormonal imbalances or fat metabolism disorders. Hormonal failure provokes an excessive accumulation of sebum (glandulae sebacea).
Other causes of atheroma:
- Seborrhea;
- Head injury with scarring of the skin near the ear
- Earlobe puncture;
- Diabetes;
- Increased sweating;
- Hypothermia or overheating as a result of solar insolation;
- Violation of hygiene rules.
As a result of the above reasons, the duct of the sebaceous gland narrows, the composition of its secretion changes, it becomes denser. The cavity of the sebaceous gland cyst increases, fat, keratinized epithelial particles, and cholesterol crystals accumulate in it. This leads to the fact that atheroma steadily increases and becomes noticeable.
Signs of atheroma near the ear

At the beginning of the development of pathology, when the sebaceous secretion thickens, but the exit from the gland is not yet clogged, subcutaneous fat can be released outward. Its increasing viscosity leads to the final blockage of the sebaceous gland duct. The process is quite slow, without pain or other unpleasant manifestations.
Symptoms of the formed atheroma:
- Rounded outline, small size;
- On palpation, an elastic formation of a dense consistency is determined, not adhered to the skin;
- Inside the capsule of atheroma there is a mushy secret (detritus);
- Atheroma may become inflamed, fester;
- The exit from the sebaceous gland can be visualized as a dark point; with inflammation of the atheroma, the exit is defined as a bulge of white color;
- Partial adhesion of atheroma to the skin can prevent the skin from gathering in a fold;
- With an increase in atheroma, itching and burning may appear;
- With inflammation of the tumor, a subcutaneous abscess develops with the appearance of pain, an increase in skin temperature in the area of suppuration, hyperemia of the epidermis;
- With a spontaneous opening of atheroma, part of the pus is released, but the cyst remains unchanged and a relapse of the tumor appears;
- The accession of a secondary infection is manifested by symptoms of intoxication - weakness, headache, increased fatigue, hyperthermia, and nausea.
In many cases, atheroma is determined completely by chance - when washing or shampooing. If a ball-like seal appears in the area of the auricle, you should immediately show the child to a doctor - a surgeon or dermatologist.
Pathogenesis of atheroma of the ear in children

A sebaceous cyst in a child may be congenital. It is always benign, according to the standard of diagnosis, it is required to differentiate atheroma from lipoma, dermoid cyst, enlarged lymph node, furunculosis.
If the child's atheroma is not congenital, its appearance can be triggered by increased production of sebaceous gland secretion at 5-6 years of age and then - during puberty. Less often, the cause of the formation of atheroma in a child is trauma to the epidermis due to improper haircut or ignorance of hygiene rules.
Atheroma behind the ear in children often does not manifest itself in any way, the child does not feel any pain or discomfort. Typical symptoms appear with inflammation and abscess formation. The abscess can be very large. If it opens, the atheroma capsule remains and provokes relapses. Only surgical intervention will help to radically get rid of it.
Atheroma of small size in children under 3-4 years old is not removed, the tumor is monitored over time. After 4 years, the atheroma capsule is husked under general anesthesia. Local anesthesia is used at the age of 7 years or older. Surgical intervention for the removal of atheroma in children lasts 30-40 minutes, it is considered a simple manipulation. This operation will avoid complications such as infection of the soft tissues of the head, the appearance of phlegmon.
There is a modern method of destruction of atheroma - its "evaporation" with a radio wave knife, leaving no marks on the skin of the child. Such treatment is very effective, as it eliminates the risk of recurrence and does not lead to scar formation.
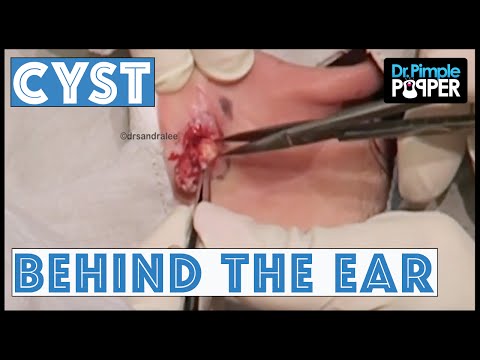
Behind the ear atheroma

Such a neoplasm appears very rarely, because the tissue behind the ear contains almost no fatty layer. Such a cyst is differentiated from atheroma of the salivary gland, using, in addition to visual examination, X-ray examination, ultrasound of the lymph nodes, computed tomography. If there are no signs of inflammation, the atheroma behind the ear is excised in the "cold period", and the extracted material is sent for histological analysis to confirm the diagnosis.
It is important to distinguish atheroma from lipoma in a timely manner, which is quite difficult, since the symptoms of the diseases are similar. Both lipoma and atheroma behind the ear have a dense consistency, they are painless. However, on the surface of an atheroma, you can sometimes distinguish a dark point at the site of the exit of the gland duct outward. With inflammation of the atheroma behind the ear, pain appears, the temperature of the skin in the area of suppuration rises.
The transformation of atheroma into an abscess or phlegmon leads to symptoms of intoxication, and this:
- Hyperthermia;
- Headache;
- Weakness, increased fatigue;
- Nausea.
With a spontaneous opening of atheroma behind the ear, pus spreads through the subcutaneous tissue, spilling into the ear canal and cartilaginous tissue of the auricle. Intoxication occurs, there is a risk of sepsis.
Removal of atheroma behind the ear is complicated by the risk of damage to the behind-the-ear lymph nodes and blood vessels.
The operation is painless and fast if modern technologies are used:
- Laser surgery;
- Radio wave surgery.
After their use, no scars remain, no relapses occur.
Atheroma on the earlobe

The appearance of a benign tumor on the earlobe is due to the fact that in this area there is subcutaneous fatty tissue, which is not present in areas with cartilage tissue. Most often, the occurrence of atheroma is provoked by damage to the tissues of the lobes during their injury, puncture. This organ is not hormone-dependent, therefore, hormonal imbalance and the onset of puberty rarely become factors that provoke the appearance of atheroma.
Other reasons for the development of atheroma on the earlobe:
- Infection of tissues with a puncture of the earlobe;
- Puncture site granulation;
- Earlobe injury in case of injury, laceration, formation of a keloid scar;
- Heredity.
Symptoms of atheroma:
- Sealing up to 40-50 mm in size;
- Lack of pain and discomfort;
- Inflammation in the process of wearing earrings or clips against the background of infection, the formation of an abscess;
- Re-accumulation of pus after spontaneous opening of the formation due to the fact that the atheroma capsule remained in place.
It is advisable to remove atheroma on the earlobe when it is small. In this case, the operation takes place quickly, without consequences, with the formation of an invisible scar. Removal of atheroma in the stage of a large cyst increases the risk of developing an abscess.
Diagnostics of the atheroma behind the ear

It is important to timely distinguish atheroma behind the ear space from such formations of subcutaneous tissue as:
- The initial stage of lymphangioma;
- Lipoma;
- Fibroma;
- Papilloma;
- Chondroma;
- Dermoid cyst behind the ear;
- Lymphadenitis;
- Furuncle of subcutaneous tissue.
Basic diagnostic methods:
- Examination and palpation of education, regional lymph nodes by a dermatologist, dermato-oncologist;
- X-ray, CT of the skull;
- Otoscopy (study of the features of the internal auditory canal);
- Ultrasound of the lymph nodes;
- Cytology of swabs from the ear canal;
- Biopsy and histology of removed tissues after surgery.
Laboratory diagnostic methods:
- General and biochemical blood test;
- General urine analysis, determination of sugar level;
- RW blood test.
The risk of malignancy of the neoplasm must be completely excluded. Although atheroma is considered a benign tumor, it must be distinguished from similar conditions that are at risk of malignancy.
Treatment of atheroma on the earlobe

Removal of atheroma involves only a surgical method of treatment. Other methods are not able to completely get rid of the tumor. Even opening the cyst and removing the sebaceous secretion that has accumulated in it will not solve the problem.
Surgical methods:
- Cyst enucleation by the traditional method - the cyst is opened under local anesthesia, its contents are removed on a sterile napkin, the atheroma capsule is excised to a healthy tissue;
- Laser surgery - used to remove small atheromas without signs of inflammation;
- Radio wave surgery - does not require long-term rehabilitation and suturing, the scar heals in a week.
After removal of atheroma in any way, the resulting tissues are subjected to histological examination.
Treatment behind the ear atheroma

A tumor of such localization can be cured exclusively by surgery. Its removal requires preliminary preparation, since the space behind the ear is rich in blood vessels, there are lymph nodes. Careful diagnosis will eliminate the risk of relapses and complications.
Methods for removing atheroma behind the ear:
- The traditional method using a scalpel is used for excision of inflamed tumors with purulent contents. The cyst is opened, drained, and after the inflammatory process subsides, the capsule is excised to healthy tissue;
- Laser method - small atheromas without signs of inflammation are removed, and blood vessels coagulate at the same time, the suture heals in 5-7 days;
- Evaporation of the tumor and the cyst cavity using the radio wave method is a gentle method that does not have complications and does not leave a cosmetic defect.
The appearance in a child of atheroma behind the ear or on his lobe is a reason to see a doctor. After a thorough diagnosis, the only possible treatment method is used - radical removal of the tumor along with the cyst membrane.

The author of the article: Volkov Dmitry Sergeevich | c. m. n. surgeon, phlebologist
Education: Moscow State University of Medicine and Dentistry (1996). In 2003 he received a diploma from the Educational and Scientific Medical Center of the Presidential Administration of the Russian Federation.
Recommended:
Impetigo - Impetigo In A Child, Causes And Treatment Of Impetigo In A Child

Causes and treatment of impetigo in a childIn a child, impetigo has several characteristic features, one of which is the high rate of spread of an infectious disease in children's groups.Impetigo refers to skin diseases and is associated with the appearance of characteristic red spots on the face, which are quite painful, scabs form in their place over time
Child's Cough Is A Dry And Wet (wet) Cough In A Child. An Attack Of Allergic Cough In A Child Without Fever

Dry and moist (wet) cough in a childContent:Dry cough in a childMoist cough in a childWet cough treatmentCoughing fits in a childCough without feverAllergic cough in a childNight cough in a childChild cough compressA cough in a child is a symptom that occurs not necessarily due to colds, but due to the fact that it is a natural reaction of the body that helps cleanse the respiratory system from dust or from chemical elements that get from the air and irritate th
Constipation In A Child - Constipation At 1 Month, What To Do If A Child Is 2-3 Years Old With Constipation? Treatment And Diet For Constipation In Children

What to do if a 2-3 year old child has constipation? Causes, treatment and dietDescription of the diseaseContent:Diagnosis of constipation in childrenCauses of constipation in childrenConstipation in an infantSigns of constipation in newbornsConstipation after complementary feedingConstipation in a child 2 years oldConstipation in children 3 years oldWhat to do if a child is constipated?
Psychosis In A Child - Signs, Causes, Diagnosis And Treatment Of Psychosis In A Child

Signs, causes and treatment of psychosis in a childPsychosis refers to complex mental illnesses, which are characterized by a violation of the ability to distinguish fantasy from reality and to consider what is happening accordingly. Psychosis of any type makes life difficult for a child
Child's Snot Is Green, Yellow, Transparent And Liquid Snot In A Child. Snot In An Infant

Snot in a childGreen, yellow, transparent and liquid snot in a childDefinition of diseaseThe appearance of snot in a child is a real problem for the child himself and for his parents. The kid immediately begins to be capricious, refuse to eat, fall asleep badly, sleep becomes very restless