2024 Author: Josephine Shorter | [email protected]. Last modified: 2023-12-16 21:43
Causes, symptoms and removal of the Bartholin gland cyst
Content:
- Bartholin gland cyst symptoms
- Causes of the Bartholin gland cyst
- Bartholin gland cyst removal
Bartholin gland cyst is a disease of the genital organs. It is an unnaturally formed cavity, within which the liquid substance of the Bartholin gland accumulates. This is due to a blockage in the excretory duct.
If the process of the disease is long, accompanied by a number of factors - weakening of the immune system, secondary infection, it means that the cyst has passed into the stage of suppuration. It quickly becomes a complicated form of the disease - an abscess of the Bartholin gland.
Certain reasons precede the cyst. The defeat of the input stream, due to which the disease is formed, occurs due to a number of factors:
- gonococcal infection;
- thrush (urogenital candidiasis);
- ureaplasmosis;
- weakened hygiene of the genitals;
- chlamydia;
- trichomoniasis.
Bartholin gland cyst symptoms

Symptoms of a Bartholin gland cyst are especially pronounced in the area where the gland develops. The labia become swollen. Formation of rounded shapes appears in them. Education differs markedly in size. They can get big enough. There is a feeling of discomfort. A small cyst is invisible, it does not interfere with sexual activity.
If the Bartholin gland becomes infected, an abscess begins. This is how the disease develops bartholinitis. Its causes lie in the penetration into the microflora of such microorganisms as gonococcal and staphylococcal infections, E. coli. With bartholinitis, the size of the labia increases dramatically. When feeling, pain occurs. When walking, an unpleasant sensation, discomfort occurs in the corresponding area. This indicates the appearance of an abscess.
In the case of an acute course of the process, the body temperature rises. The cyst grows, it can reach 8 cm in diameter with an abscess. In this state, there is a risk of its self-opening.
Causes of the Bartholin gland cyst
The causes of the cyst of the Bartholin gland are associated with chronic inflammation of the gland of the vestibule, which also captures its ducts. Such a pathogenic process is often associated with infections and concomitant diseases of a certain area:
- trichomoniasis,
- ureaplasmosis,
- mycoplasmosis,
- gonorrhea,
- candidiasis
- chlamydia.
Nonspecific opportunistic microorganisms enter the tissues and cells of organs, accompanied by a general deterioration in the body's resistance.
Infection of the body and the tissues of the gland itself is usually preceded by the absence or poor adherence to intimate hygiene, a case of injury to the epidermis due to epilation of a deep bikini, skin irritation obtained mechanically due to tight underwear, etc. Hematogenous development of infection is a characteristic background for chronic inflammation - tonsillitis, sinusitis, pyelonephritis, etc.
Often this disease develops together with bartholinitis or a cyst of the Bartholin gland, which is favorable for this. Among the common reasons is surgical termination of pregnancy. No less frequent are cases when such a cyst is formed after recent intercourse.
Bartholin gland cyst removal (operation)
Removal of the Bartholin gland cyst is performed under certain indications. Among them:
- development of a tumor of the labia minora,
- inflammation with suppuration,
- pressing painful sensations of the external genital organs.
The operation is performed on the day of treatment, without prior preparation. When the formation bursts, causing a sensation of soreness, it is recommended to completely remove the bartholin gland, followed by a course of antibiotics.
Traditional drainage is rarely performed due to frequent dangerous relapses. With such an operation, the duct is blocked with a special catheter, which is removed only after complete healing with epithelialization.
In most cases, surgery to remove a Bartholin gland cyst is performed under local anesthesia. The only contraindication for this is increased soreness. Then general anesthesia is applied. The choice of anesthesia is determined by the doctor.
There are complications when it is necessary to remove the entire organ. Together with the Bartholin gland, its duct is also removed (excision). This is a technique used only in extreme situations. Before that, they try to get the desired result from more gentle methods.
Marsupialization of the Bartholin gland cyst is a measure by which recurrent inflammation of the Bartholin gland is treated. A surgical operation is based on a new formation of a duct with an opening. The operation to marsupialize the cyst is carried out in order to restore the patency of the excretory duct, improve the functionality of the Bartholin gland, eliminate post-inflammatory consequences and prevent abscess formation of the cyst cavity.
If a site appears to be the most swollen, an incision is made on the mucous membrane, the same is done on the cyst. Then the cavity is washed with medical methods. As a result of the entire procedure, the cyst membrane is sewn to the area of the mucous membrane of the labia. This helps to form the excretory duct.
An autopsy of the cyst is often suggested. In this case, the contents are removed, washing is carried out. The epithelium does not have time to be covered with a protective film. It is harmful and often leads to relapse. The blockage of the duct will occur again, and the cyst will re-form. More modern is the installation of a special catheter, in which a bubble is formed inside. It should be installed after surgery to open the cyst for a period of several weeks. This is enough to create a new channel. As a result, the risk of relapse is markedly reduced.
For such interventions, local anesthesia is needed. Then the patient can immediately return home. Sexual contact is prohibited for the next month.
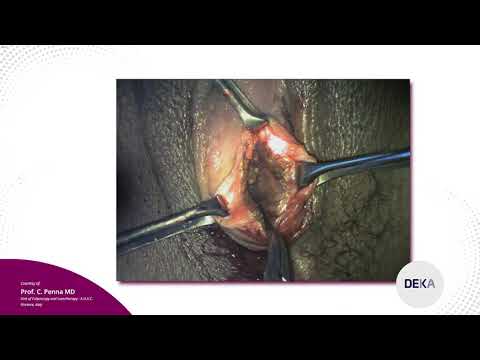
Hulling a cyst of the Bartholin gland is a special operation. An incision is made on the surface, heading from the small lip. The opposite direction is dangerous, in this part of the body the mucous membrane lining the entrance to the vagina is tender and often depleted from disease. Let's say a cyst capsule incision. If the incision is made correctly, the edge areas diverge by 0.5 cm.
Hulling of the cyst of the Bartholin gland is carried out with the removal of the incised fiber. Use Pean clamps and gauze swabs. To squeeze out the contents, the fiber is carefully cut. Such an operation is performed with caution. Do not allow the cyst to rupture, then the operation will slow down, and this contributes to the contamination of the surgical wound. In order to sew up the cyst holes, two sutures are enough. In such an operation, the gland is removed.
When hulling is performed, the patient loses a lot of blood. It can be stopped with great care. Branches, weakening from hemorrhage, are bandaged. Venous wounds are closed with tourniquets. They need to completely cover the cyst bed. After applying tourniquets, the submerged sutures are removed, the Peana clamps are removed from the edges of the incision. There comes a period when the epidermis is retracted. The wounds are markedly reduced in size. The edges of incisions and wounds are fastened with vicryl.
The postoperative period may be complicated by vulvar edema. It disappears in a few days. To achieve the prevention of the Bartholin gland as a whole, you need to take care of increasing immunity. You also need to monitor personal hygiene, treat thrush on time, and adhere to a healthy diet.

The author of the article: Lapikova Valentina Vladimirovna | Gynecologist, reproductologist
Education: Diploma in Obstetrics and Gynecology received at the Russian State Medical University of the Federal Agency for Healthcare and Social Development (2010). In 2013 completed postgraduate studies at N. N. N. I. Pirogova.
Recommended:
Cyst In The Nasal And Maxillary Sinus - Removal And Treatment

Cyst in the nasal and maxillary sinusContent:Signs and symptoms in the sinusCauses of a cyst in the sinusTreatment of a cyst in the sinusRemoval of a cyst in the sinusTreatment of cysts with folk remediesA maxillary sinus cyst (maxillary cyst) is a small, hollow, benign mass with elastic walls that contains fluid inside
A Cyst On The Gum Of A Tooth - Symptoms, Consequences And Treatment Of A Cyst On The Gum With Folk Remedies, Removal

Causes, consequences and treatment of cysts on the gum of the toothContent:Symptoms of cysts on the gumsCauses of cysts on the gumsThe consequences of a cyst on the gumSurgery to remove a cyst on the gumTreatment of cysts on the gums with folk remediesA cyst on the gum is a neoplasm of a certain size that is filled with purulent fluid
Removal Of Atheroma: Does It Hurt? Removal Types, Consequences

Removal of atheroma: types of surgery and consequencesAtheroma is a sebaceous cyst that can form in almost any part of the body. The only place where it never occurs is the feet and palms, which do not have corresponding glands on their surface
Knee Cyst - Baker's (baker's) Cyst, Treatment And Surgery

Knee baker cyst treatment and surgeryContent:Signs and symptoms of a knee cystKnee cyst causesBaker's cyst of the kneeOther types of knee cystsKnee Cyst TreatmentKnee cyst removal (surgery)A cyst of the knee joint is a tumor-like benign formation that is localized on the back wall of the joint and is an accumulation of joint fluid
Laser Lipoma Removal - What And How It Goes, Indications And Contraindications

Laser lipoma removalLaser removal of a lipoma is a surgical treatment of a neoplasm, one of the most effective and safe ways to remove a tumor. During the operation, pathological cells are excised together with the capsule. Healthy body tissues remain intact