2024 Author: Josephine Shorter | [email protected]. Last modified: 2024-01-07 17:49
High blood pressure medications

One of the main risk factors for the onset of hypertension is considered a high blood pressure, the norms of which differ for patients of different age categories. Modern doctors consider blood pressure above 140/90 at any age pathological and requiring control. Moreover, drug treatment is not necessary in every case.
So, in the absence of concomitant pathologies - endocrine disorders, diabetes mellitus, cardiac disorders, when constantly high blood pressure is observed, the patient's condition can be corrected without resorting to medications. In the early stages of the disease, it is enough to change the diet, lose weight, and exercise more often. Psychotherapy, reflexology, massage, meditation are considered to be effective methods of non-drug treatment of arterial hypertension in the early stages. However, when the pressure rises above the border of 160 to 90, such treatment methods are no longer enough.
Another factor that is taken into account when drawing up a course of treatment is target blood pressure, that is, the results that need to be achieved. Targets for most patients range from 140-135 to 90-85. If earlier it was allowed to slightly increase the norms for elderly patients, now these figures are universal for all patients with arterial hypertension.
There are differences in the approach to the treatment of older patients with complications in the form of atherosclerotic plaques - it is necessary to reduce the pressure to the target values gradually in order to avoid health problems.
In mild cases of arterial hypertension in patients under sixty, as well as in people with renal failure and diabetes mellitus, it is necessary to adhere to the boundaries of 120-139 by 85 mm Hg.
Classification of risk factors for arterial hypertension:

- The presence of endocrine disorders and systemic diseases, diabetes mellitus;
- Hereditary factors - relatives with coronary heart disease at an early age and other pathologies;
- Increased cholesterol level (more than 6.5 mmol / L);
- Bad habits - excessive alcohol consumption, smoking;
- Cardiac disorders, coronary heart disease, myocardial infarction;
- Age over 55 for men and over 65 for women;
- Persistent increase in blood pressure.
Factors contributing to the development of arterial hypertension:
- Renal failure, nephropathy;
- Environmental factors - life in the urbanized space of large cities;
- Obesity and sedentary lifestyle, lack of a minimum level of physical activity;
- Disorders of glucose metabolism;
- Microalbuminuria.
Factors that increase the risk of mortality in patients with arterial hypertension:
- Cerebral circulation disorders - stroke, history of ischemia;
- Cardiac disorders - ischemic heart disease, myocardial infarction;
- Circulatory disorders in the retina, hemorrhagic disorders, edema of the optic nerve.
"Death Quartet" of symptoms:
- Pathological excess weight;
- Increased cholesterol levels;
- Increased blood sugar levels;
- Obesity.
Most underestimate the risks of illness, do not get regular check-ups, and refuse medication and other lifestyle changes. With exacerbations of high blood pressure, they prefer to endure discomfort and refuse medical intervention, which poses a threat to life and increases the risk of sudden death from a catastrophe in the cardiovascular system.
There is another group of patients who understand the risk of the disease based on the experience of relatives and friends who have had a heart attack or stroke. They resort to self-medication, buying up all the newfangled drugs for high blood pressure in pharmacies without a doctor's prescription, and will try these remedies on themselves. However, they do not want to entrust their treatment to a specialist.
At the same time, in both cases, the optimal solution would be an examination by a specialist who has extensive practice in the treatment of arterial hypertension and can draw up an individual course of treatment using modern drugs. This avoids irreversible changes in internal organs and reduces the risk of sudden death.
Content:
- Drugs for hypertension
- Thiazide diuretics and sulfonamides
- Beta-blockers
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors
- Sartans (angiotensin II receptor blockers)
- Calcium channel blockers
- Central antihypertensives
- Why is it impractical to use rauwolvia preparations?
- Relief of a hypertensive crisis
- Hypertension in the elderly
- Treatment of resistant hypertension
Drugs for hypertension

Drug treatment of hypertension is necessary with a persistent increase in pressure above 160 to 90 mm Hg, for patients with concomitant pathologies - cardiac dysfunction and renal failure - indicators from 130 to 85 mm Hg are dangerous. and higher.
In most cases, multiple drugs are used to treat hypertension. Combined therapy allows a complex effect on the mechanisms of the development of the disease and mitigates the severity of side effects. At the same time, the dosage of drugs for high blood pressure can be reduced due to their synergistic action, which ensures maximum effectiveness. However, in the case of mild arterial hypertension with increased heart pressure, one single-action drug can be dispensed with, which is taken once a day.
Thiazide diuretics and sulfonamides
Saulretics contain sulfonamides and thiazide diuretics, which together improve urine output and remove puffiness. When the edema of the vascular wall subsides, the lumen of the vessel increases and the blood flow is facilitated, respectively, the pressure decreases.
Thiazides

- Cyclomethiazide;
- Hydrochlorothiazide;
- Hypothiazide.
The mechanism of action is based on blocking the reabsorption of sodium and chlorine, which occurs in the renal tubules. Thus, excess fluid is not retained in the body, and the puffiness subsides.
When used by people with normal blood pressure, they do not change its indicators.
The first effect occurs one and a half hours after administration, the duration of action is from 6 to 12 hours.
The dosage of the drug for monotherapy is 25-50 mg, with combined therapy, the doses range from 12.5-25 mg. Take the drug in the morning.
Contraindications: electrolyte imbalance, pregnancy and lactation, anuria, renal and hepatic failure, age less than 3 years, Addison's disease.
Side effects: nausea, dry mouth and dizziness, cramps and muscle pain, electrolyte imbalance, allergic rashes, anaphylactic shock, photodermatitis, temporary visual impairment, numbness of the extremities, pulmonary edema, Steven-Johnson syndrome, pneumonitis, hemolytic anemia, disorder potency, arrhythmia, diarrhea, nausea and vomiting, exacerbation of gout and cholecystitis, renal failure, interstitial nephritis.
Sulfonamides

Sulfonamides are well tolerated by patients, prevent cardiovascular complications and reduce the risk of sudden death. Completely excreted from the body through the liver and kidneys, do not accumulate in organs and tissues.
- Chlorthalidone or Oxodoline;
- Indapamide - prescribed to patients with diabetes mellitus, since it does not change blood sugar levels;
- Chlorthalidone and Atenolol as part of a combination drug.
Drugs in this group are prescribed in severe cases of arterial hypertension, in which other medications are ineffective. They are used as part of a combination therapy, and Chlorthalidone in Russia can only be purchased as a complex with other drugs.
Method of administration and dosage: Indapamide is taken once a day, regardless of meals, a single dosage is 2.5 mg, the duration is 24 hours. The effect of the use of the drug is manifested after 7 days from the start of admission.
Contraindications: pregnancy and lactation, a decrease in the level of potassium in the blood, electrolyte imbalance, lactose intolerance and severe forms of renal, hepatic failure.
Side effects: on the part of the digestive system, nausea and vomiting, stomach pains and stool disturbances may occur; from the nervous system - insomnia or drowsiness, nervousness, depression. Other possible side effects are allergic rashes, a sharp drop in blood pressure, heart palpitations, dry cough, rhinitis, and pharyngitis.
Beta-blockers

This group includes drugs for which the ability to reduce the risk of cardiovascular problems has been reliably determined. The use of beta-blockers is possible for patients who have experienced myocardial infarction, suffer from angina pectoris, chronic heart failure, or permanent atrial fibrillation. The therapeutic effect is achieved by blocking beta receptors and reducing the intensity of the release of angiotensin 2 and renin - hormones that cause vasoconstriction.
Beta-blockers can be taken as part of both mono and combination therapy. The period of isolated administration of these drugs usually does not exceed one month - after this period, a combination with calcium channel blockers or diuretics is required.
Beta-blockers are divided into two groups:
- Non-selective: carvedilol, oxprenolol, sotalol (SotaHexal), nadolol (Korgard 80), propranolol (Anaprilin);
- Selective: atenolol, betaxolol, nebivolol, bisoprolol, metoprolol, celiprolol.
If long-term treatment is required, metho- and bisoprolol, nebivalol, betaxolol and carvedilol, which significantly affect the risk of death in hypertension, are the best. Betaxolol (Lokren drug) is recognized as the drug of choice for combating hypertension in women during menopause.
Carvedilol

It is the most common non-selective adrenergic blocker and the main active ingredient in a wide range of drugs:
- Carvedilol;
- Cariol;
- Kardivas;
- Dilatrend;
- Acridilol;
- Bagodilol;
- Vedicardol;
- Carvedil;
- Carwenal;
- Talliton;
- Atram;
- Recardium.
The effectiveness of carvedilol, in comparison with other beta-blockers, is increased by blocking vascular receptors not only of the beta, but also of the alpha type.
Reception of funds is calculated from the daily need for 25-50 mg of carvedilol.
Contraindications relate to heart problems such as blockade, infrequent rhythm and decompensated insufficiency, as well as pathologies such as bronchial asthma and various liver damage. The drug is not prescribed if the patient is under 18 years of age, and women during lactation. In depressive conditions, pregnancy, renal failure, psoriasis, diabetes mellitus and thyrotoxicosis, prescribing drugs with carvedilol is possible only with caution on the recommendation of the attending physician.
The most likely side effects of the drug:
- a sharp drop in blood pressure;
- desiccation of the oral mucosa, vomiting and violations of the regime and quality of the stool are also possible;
- bradycardia;
- various reactions of an allergic nature: runny nose, spasms of the upper respiratory tract, redness and rashes on the skin, sneezing, weight gain, flu-like syndrome and pain in the extremities.
Bisoprolol

Produced in such pharmaceuticals:
- Aritel;
- Bisoprolol;
- Biol;
- Bisogamma;
- Biprol, Bidop Cor;
- Coronal;
- Concor;
- Cordinorm;
- Niperten.
Bisoprolol should be taken in the morning in an amount of 5 to 10 mg, although with mild hypertension, a dose of more than 2.5 mg per day is not required. A feature of the drug is the need to gradually reduce the dosage over two weeks, since an abrupt cessation of the course often provokes sharp surges in blood pressure. Due to the similar pharmacokinetics, contraindications and the list of side effects of bisoprolol are similar to those for carvedilol.
Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors
They act on the enzyme responsible for the conversion of the vasoconstriction hormone angiotensin into renin. As a result, there is a decrease in blood flow through the heart, restoration of the myocardium in the presence of hypertrophy, and prevention of its thickening occurs.
ACE inhibitors with sulfhydryl group

This category includes substances such as:
- Captopril (drugs Capoten, Epsitron, Captopril, Alkadil);
- Benazepril (Potenzin);
- Zofenopril (Zokardis drug).
Captopril is one of the best remedies for hypertensive crises, but because of its strong effect, it is better not to take it to elderly people with vascular atherosclerosis.
Contraindications: Quincke's edema during therapy with ACE inhibitors in history, pregnancy, lactation, children under 18 years of age, after kidney transplantation, difficulty in the outflow of blood from the LV, with caution in diabetes mellitus, cerebral ischemia, coronary artery disease, old age, severe autoimmune diseases.
ACE inhibitors with carboxyl group

This group of ACE inhibitors includes:
- Enalapril - represented by the drugs Enalapril, Enap, Enam, Edith, Berlipril, Renipril, Renitek;
- Lisinopril - Lisinopril, Lisinoton, Diroton. The drug of choice if the patient has type 2 diabetes mellitus and metabolic syndrome.
- Perindopril - Prestarium, Perineva. In addition to combating hypertension, it has proven itself well in the prevention of stroke, as well as a drug for hypertensive patients with chronic heart failure;
- Spirapril - Quadropril;
- Ramipril - Hortil, Tritace, Amprilan;
- Trandolapril - Terka Retard;
- Cilazopril;
- Quinopril.
Practice shows that in addition to the main action, enalapril is able to literally prolong the patient's life. At the same time, among the side effects, the most unpleasant is a dry cough.
At the same time, Enalapril from the manufacturer Nizhpharm (crushed chalk) has not a single proven case of patient benefit from its use. This once again shows that the original drugs are much more preferable than their cheap counterparts.
Contraindications: pregnancy, lactation, hypersensitivity, with caution - diabetes mellitus, hepatic, renal failure, old age, children under 18 years of age, ischemic heart disease, severe autoimmune diseases, after kidney transplantation, etc.
Application: initial dose of 5 mg. 1 r / day, if there is no effect after 2 weeks, the dose is increased to 10 mg. With moderate hypertension, the daily dose is 10 mg, the maximum daily dose is 40 mg.
Side effects: decreased pressure, angina pectoris, arrhythmias, pulmonary embolism, headache, dizziness, depression, nervousness, increased fatigue, tinnitus, impaired vision and hearing, vestibular apparatus, decreased appetite, dyspepsia, pancreatitis, jaundice, dry cough, shortness of breath, pharyngitis, bronchospasm, Quincke's edema, urticaria, photosensitization, stomatitis, arthritis, arthralgia, impaired renal function, hair loss, decreased libido.

|

|

|
|
Indicated for the prevention of recurrent stroke, with chronic heart failure, with stable coronary artery disease, with arterial hypertension |
Lisinopril 20-70-170 rubles, Lizinoton 160-220 rubles It is the drug of choice in elderly patients with metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes. |
Fozinopril (Monopril 350 rubles, Fozicard 120-200 rubles) Fosinopril is the drug of choice for renal failure and severe renal disease, since renal pathology does not require dose adjustment. |
With a phosphinyl group
These ACE inhibitors are found in the drugs Fosinopril, Fosicard.
Essential for the treatment of hypertension in renal failure.
Sartans (angiotensin II receptor blockers)

Modern drugs for high blood pressure, which made themselves known on the pharmaceutical market in the early nineties. They differ in effective pressure reduction for a whole day (maximum - for 48 hours), act gently, dry cough manifests itself in very rare cases, there is no withdrawal syndrome. They relieve spasm of the walls of blood vessels, due to which they can be used for renal hypertension.
List of common sartans:
- Losartan is considered the best original sartan available in the Russian Federation. The main active ingredient of drugs such as: Losartan, Lorista, Lozarel, Lozap, Bloktran, Vasotenz, Kozar, Prezartan, Teva;
- Valsartan - available in Valsakor, Valz, Diovan medicines;
- Eprosartan - Teveten;
- Candesartan - Atakand;
- Telmisartan - Twinsta and Mikardis.
Losartan is the leading original sartan in Russia.
Contraindications: dehydration, childhood, pregnancy, lactation, hyperkalemia.
Application: once a day, 50 mg, the dosage may be increased to 100 mg.
Side effects: insomnia, headache, dizziness, migraine, ringing in the ears, memory disorders, loss of consciousness, vision changes, cough, nasal congestion and bleeding, bronchitis, chest pain, back pain, arthritis, arrhythmias, palpitations, anemia, decreased libido, dry skin, hair loss, increased sweating, Quincke's edema, fever, gout, etc.
Calcium channel blockers

Specific drugs that have a positive effect on the ability to tolerate physical activity. They play an important role in combination with ACE inhibitors, as they allow you to do without diuretic drugs. They can be used to treat patients with cerebral atherosclerosis and a combination of hypertension, angina pectoris and cardiac arrhythmias.
They are divided into three types:
- Dihydropyridines (eg, amlodipine, nifedipine);
- Benzodiazepines (eg diltiazem);
- Phenylalkylamines (e.g. verapamil)
The following drugs have proven themselves well:
- Amlodipine - is available in Amlodipine, Amlotop, Amlovas, Tenox, Norvask, Kolchek, Cardilopin preparations. Take 5 or 10 mg per day.
- Verapamil - medicines Verapamil, Isoptin, Verogalid;
- Nifedipine - Osmo-adalat, Nifecard, Cordaflex, Cordipin, Calcigard, Fenigidin;
- Diltiazem - Diltiazem, Diazem, Diakordin, Cardil.
Contraindications: pregnancy, lactation, hypersensitivity, with caution in liver failure, old age, children under 18 years of age, acute myocardial infarction.
Usage: 5 mg / day, maximum daily dose 10 mg / day.
Side effects: in addition to those listed above, rarely occur - nosebleeds, cold sweats, skin pigmentation, pain in the eyes, painful urge to urinate, etc.
Central antihypertensives
The most popular drugs for high blood pressure in this group are clonidine, moxonidine and andipal.

|

|

|
Why shouldn't you use rauwolvia preparations?

Rauwolfia drugs, the most common of which are Raunatin and Reserpine, are some of the earliest treatments for hypertension. They belong to the group of sympatholytics, they retain sodium and excess fluid in the body.
The therapeutic effect of taking rauwolfia drugs comes very slowly - the hypotensive effect becomes pronounced only in the second week of admission, and only 25% of patients achieve stable results in stabilizing normal blood pressure.
Moreover, this group of drugs does not meet the basic requirements for modern drugs for the treatment of arterial hypertension - improving the patient's quality of life and minimizing the risks of complications from the cardiovascular and other body systems. Thus, modern drugs can prevent the development of atherosclerosis and the formation of plaques on the walls of blood vessels, prevent arrhythmia and sclerotic formations in the renal glomeruli, and reduce left ventricular hypertrophy.
Rauwolfia preparations are still used by many patients with arterial hypertension, focusing on their affordable price. However, the main reason why these drugs should be abandoned is the pathologies that may arise after their use.
These include:
- High risk of developing malignant tumors in the mammary glands. The incidence of the disease increases by 3 times in people taking drugs based on reserpine;
- Reserpine drugs contribute to the development of cancer in the pancreas, as proven by scientific research. This is the main reason for the banning of rauwolfia preparations in several European countries, including France.
Side effects that appear after using reserpine drugs:

- Bronchial cramps, nasal congestion;
- Sleep disorders, depression, in elderly patients while taking the drug, parkinsonism may occur;
- Cardiac disorders, arrhythmia;
- Peptic ulcer, gastrointestinal tract pathology;
- Puffiness;
- Impotence.
There are combined forms of drugs based on rauwolfia, which increase the effectiveness of the main active ingredient. However, this happens mainly due to the diuretic components in the composition of the drug, while the number of side effects does not decrease, but is summed up from all the components of the drug.
The combined forms of rauwolfia include:
- Sinepres (reserpine, hydrochlorothiazide, dihydroergotoxin);
- Adelfan (combination of reserpine and dihydralazine);
- Brinerdin (reserpine, dihydroergotoxin, clopamide and dihydroergocristine);
- Trireside (contains reserpine, hydrochlorothiazide, digralazine and potassium chloride);
- Adelfan esidrex (reserpine with hydrochlorothiazide and dihydralazine).
Due to the availability of modern drugs for the treatment of arterial hypertension at an affordable price for most patients, it is impractical to use Rauwolfia drugs. They are inferior in effectiveness to modern drugs and have many side effects, which makes it all the more difficult to use them in the treatment of elderly patients in whom the severity of side effects on the central nervous system and mental state is maximal.
Hypertension in the elderly

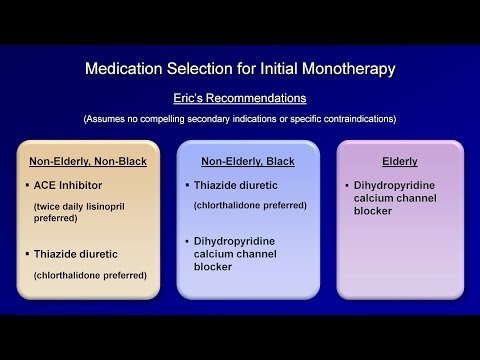
For the treatment of hypertension in elderly patients, diuretics are primarily prescribed - hypothiazide and indapamide. Indapamide is prescribed to patients with diabetes mellitus. Monotherapy with these drugs gives good results in mild forms of hypertension, and their low cost makes these drugs available to most people. In addition, these high blood pressure medications are effective in treating hypertension in postmenopausal women.
Second-line drugs include dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers - nifedipine and amlodipine. They are prescribed to patients with overweight and concomitant pathologies in the form of diabetes mellitus and atherosclerosis.
Third-line drugs - sartans and lisinopril.
Drugs for the combination therapy of arterial hypertension - tarka (trandolapril with verapamil) and prestan (perindopril with amlodipine).
Relief of a hypertensive crisis

Modern medicine no longer recognizes the classical method of relieving hypertensive crises with the help of intramuscular injection of magnesium sulfate, since the injection requires too much time, special skills and resources (sterile syringe, container with the drug, etc.).
It is much more effective to stop the crisis with the help of modern pharmaceuticals:
- Nifedipine (or Corinfar) - a tablet with 10 or 5 mg of active ingredient, dissolves under the tongue;
- Kapoten - required in an amount of 25-50 mg, is also taken in the form of tablets for absorption under the tongue, recognized as the best drug against hypertensive crisis;
- Physiotens (or moxonidine) - 0.4 mg;
- Clonidine (or clonidine) - 0.075 - 0.15 mg.
- Clonidine also does not meet modern quality standards for medicines, therefore it is prescribed only in the case of chronic patient intake.
Hypertension in the elderly
- The most important drugs for high blood pressure are diuretics: hypothiazide or indapamide (for diabetes). Cheap, but effective drugs allow their use for one-component treatment of mild hypertension. They are also preferred for volume-dependent hypertension in menopausal women.
- The second most important are calcium channel blockers of the dihydropyridine series (amlodipine, nifedipine), which are indicated for atherosclerosis and diabetes mellitus against the background of weight problems.
- Third place - lisinopril and sartans.
- Combined drugs: Prestans (Amlodipine + Perindopril), Tarka (Verapamil + Trandolapril).
Combination therapy

Combination therapy of hypertension involves the simultaneous administration of various types of drugs, the most popular and effective of which are:
- Diuretics and ACE inhibitors. Combinations of drugs from these groups - ramipril-hypothiazide (amprilan, hartil), lisinopril-hypothiazide (iruzid), enalapril-indapamide (enzix), enalapril-hypothiazide (enap NL, berlipril plus), captopril-hypothiazide (capopril-plus), peri- noliprel).
- Diuretics and sartans. Combinations of the following drugs: gizaar (losartan-hypothiazide), atacand plus (candesartan-hypothiazide), micardis plus (telmisartan-hypothiazide), coaprovel (iprosartan-hypothiazide).
- Diuretics and beta-blockers. The combination of bisoprolol with hypothiazide (bisangil) is used to minimize the risk of complications from the cardiovascular system.
- Diuretics with calcium channel blockers. The most popular combination is chlorthalidone and atenolol.
- Calcium channel blockers with sartans. Combinations of the following drugs: telmisartan with amlodipine, losartan with amlodipine.
- Ca-channel blockers together with angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors. This combination can also be used to treat resistant forms of hypertension, since the use of these drugs does not reduce the body's sensitivity to medications. Includes the following combinations: amlodipine with perindopril, trandolapril with verapamil.
Treatment of resistant hypertension

Resistant arterial hypertension is a form of the disease in which it does not respond to treatment with monotherapy, and even therapy with a combination of drugs from two different groups does not give results.
To normalize pressure readings, the following combinations of pharmaceuticals with different properties are used:
- Beta blockers, dihydroperidine calcium channel blockers, ACE inhibitors;
- Beta-receptor blockers, calcium channel blockers and sartan;
- Diuretics, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors, Ca channel blockers.
The third regimen, combining the use of diuretics and Ca-channel blockers together with ACE inhibitors, is considered the best treatment for refractory hypertension. For these purposes, a combination of spironolactone and thiazide diuretics is also used.
In view of the existence of a huge list of drugs and treatment regimens for arterial hypertension with medicines that are used for different forms of the disease and are prescribed individually, self-medication can be not only ineffective, but also dangerous to health. A timely visit to a doctor minimizes the risk of stroke, heart attack (causes and symptoms of myocardial infarction) and other complications of the disease.

Author of the article: Alekseeva Maria Yurievna | Therapist
Education: From 2010 to 2016 Practitioner of the therapeutic hospital of the central medical-sanitary unit No. 21, city of elektrostal. Since 2016 she has been working in the diagnostic center No. 3.
Recommended:
Blood Sugar Rate - High And Low Blood Sugar

Blood sugar rateBlood glucose is a sugar that is carried by the bloodstream to all cells in the body to supply them with energy. The body regulates blood glucose levels so that they remain moderate: enough to fuel cells, but not enough to overload blood flow
High Blood Pressure With Hypotension, What To Do?

High blood pressure with hypotension, what to do?Hypotension is a persistent drop in blood pressure. Typically, hypotensive patients have a consistently low blood pressure of 100 to 60 mm. rt. Art.Most often, hypotension is observed in young people
High Blood Pressure - Causes, Signs, Symptoms. What To Do With High Blood Pressure?

High pressureCauses, signs and symptoms of high blood pressureContent:What is pressure?High blood pressure reasonsRisk factorsHigh blood pressure symptomsHigh pressure treatmentWhat to do with high pressure?Complications of high blood pressureWhat is pressure?
Low Blood Pressure Tea - Does Green Tea Lower Blood Pressure?

Teas that lower pressureOne of the main signs of life is blood pressure, that is, the pressure exerted by blood on the walls of blood vessels. There are several types of blood pressure: arterial, capillary, intracardiac, venous. Arterial pressure is an important parameter that characterizes the work of the entire blood system
Low Blood Pressure - Causes, Signs, Symptoms. What To Do With Reduced Pressure?

Causes, signs and symptoms of low blood pressureLow blood pressure is a condition accompanied by a drop in blood pressure below 120 to 80 . The WHO indicates that any indicator below 100/60 mm Hg. Art. is low pressure. But here it is necessary to proceed not from standardized indicators, but to make exceptions due to the individual characteristics of the organism