Causes and symptoms of damage to the internal meniscus
Related articles:
-

Image -

Image -

Image -

Image -

Image

The crescent-shaped lining of cartilage between the shin and thigh is called the meniscus. Its main function is to cushion, stabilize and limit excessive activity of the knee joint, as well as to reduce the friction of the joint surfaces.
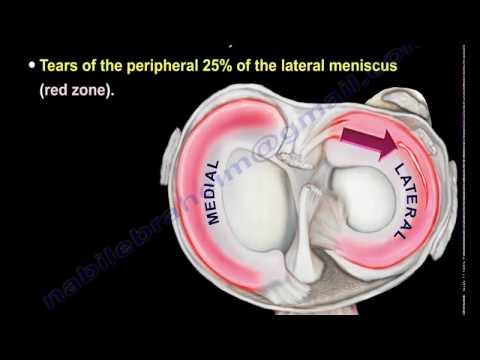
There are two menisci in the knee: the lateral or external, which is most mobile and less subject to injury, and the medial or internal less mobile, associated with the internal ligament of the knee located on the side. Movement of the knee causes compression of the menisci, changes their shape.
Causes of damage to the internal meniscus
The internal meniscus is often damaged. The most common cause of abnormalities in the knee joint is injury associated with a ruptured meniscus. People who go in for sports (skiers, football players, figure skaters, etc.), professional dancers engaged in hard physical labor are often subjected to such violations. The age category ranges from 18 to 40 years old, mostly men. Children under the age of fourteen have certain features of anatomy and are rarely subject to such injuries.
The reason for the meniscus rupture can be the presence of degenerative and inflammatory processes in the knee joint, for example, microtrauma, arthrosis, rheumatism, as well as the presence of chronic intoxication, gout. These disorders are common in older people, and work associated with walking and standing is an aggravating factor. Internal meniscus injury can be combined with ligament rupture and other structural damage to the knee joint.
Symptoms of damage to the internal meniscus
The acute period of the disease is characterized by nonspecific inflammation, soreness of the local type, a sharp restriction of movement, accumulation of blood or exudate in the cavity. The absence of characteristic symptoms makes diagnosis difficult. A single trauma has tears, infringement, bruises, sometimes the meniscus is crushed, which is not accompanied by separation and separation from the capsule. After 15-20 days, the phenomena of a reactive nature gradually subside and signs specific to the meniscus problems appear. The presence of effusion is felt, the capsule is infiltrated and pain in the articular ridge, which manifests itself at the level of the articular space. As a consequence of a pinched meniscus, joint immobility and muscle atrophy of the thigh and lower leg may appear.
Simple tests can confirm damage to the inner meniscus. These include pain that occurs when trying to go downstairs, when trying to sit "in Turkish", when making rotational movements keeping the knee bent at a right angle, when pressing on the joint space at the time of extension of the knee, which was bent at an angle of 90 °.
The chronic period of the disease occurs with constant microtrauma of the internal meniscus. There are no pronounced symptoms in this process. Typical is the periodic appearance of synovitis, the occurrence of atrophy of the quadriceps rib muscle, pain that forms along the joint gap. The reason for the development of minispathy may be disturbed statics, that is, flat feet, varus or valgus knee, and so on.
Diagnosis of damage to the internal meniscus
Making an accurate diagnosis requires a visual examination, questioning the patient in order to identify the mechanism of injury. The orthopedic surgeon then performs certain tests to get a complete picture of the clinical symptoms. The diagnosis is clarified by the data of magnetic resonance imaging of the knee joint, which make it possible to understand the general picture of the state of the joint and the formations adjacent to it. This is necessary to determine the tactics of treatment, since MRI examines the injury in several planes and provides data with high accuracy.
Treatment of damage to the internal meniscus

The method of treatment is chosen depending on how severe the condition and extensive trauma the patient has. Minor trauma, microtrauma and degenerative changes in the meniscus are treated with conservative methods and only in quite rare cases is surgery used. In case of serious injury, both conservative and surgical treatment is used. It all depends on the results of the diagnosis, and the decision is made by the doctor, taking into account the symptoms, the professional factor, the degree of stress, the sports level of the patient.
A ruptured internal meniscus usually requires surgery. During the operation, the torn meniscus is sutured and refixation or arthroscopic resection is carried out; in certain cases, the detached part of the meniscus is partially removed or its complete removal is carried out. When prescribing an operation, some factors are taken into account: the patient's age, the duration of the injury, the location of the rupture, the stability of the knee joint. Depending on the complexity of the operation, the recovery period, when the load on the joint is limited, takes 3-6 weeks.

Article author: Mochalov Pavel Alexandrovich | d. m. n. therapist
Education: Moscow Medical Institute. IM Sechenov, specialty - "General Medicine" in 1991, in 1993 "Occupational Diseases", in 1996 "Therapy".