Complications with flux
Dental periostritis (flux) is a doubly dangerous disease. Severe in itself, it can lead to complications. Periostitis can develop into an abscess or phlegmon - the most dangerous form of the disease.
With periostitis, pus concentrates near the periosteum, while with an abscess, it spreads wider. With the development of phlegmon, purulent accumulations can infinitely penetrate between the muscles of the face and neck.
Abscess

An abscess is a limited focus of purulent accumulation. The first symptom is toothache in the area of the affected tooth. Pressing on it causes increased pain. After a while, compaction and swelling of soft tissues appear.
With the progression of the purulent process, there is a deterioration in the general condition, an increase in body temperature, a violation of appetite and sleep.
Pus with an abscess can eventually break out. In this case, the pain will subside, the asymmetry of the face will disappear, and the general well-being will improve. However, this is only an external restoration. The infection doesn't go anywhere. The painful process takes on a chronic form. Bad breath appears, and intoxication of the whole organism increases.
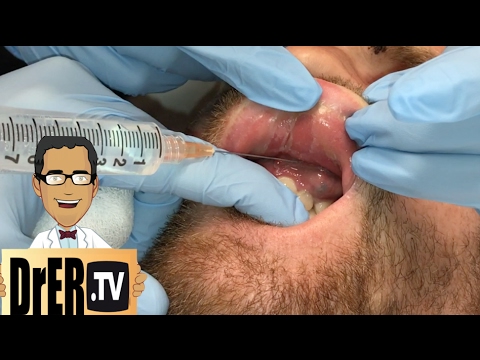
In the initial stages, with a satisfactory condition, the patient is prescribed conservative treatment. But at a more advanced stage, to eliminate the focus of infection and to prevent its spread to the surrounding tissues, it is necessary to surgically open the abscess, otherwise there is a risk that the limited inflammation will develop into a diffuse one. In this case, the abscess passes into a phlegmon.
Phlegmon

Phlegmon is a purulent inflammation of the cellulose. Periomandibular phlegmon affects the maxillofacial region. With a superficial form of the disease, the subcutaneous tissue becomes inflamed, with a deep one - intermuscular tissue.
Bacteria such as staphylococci, streptococci, anaerobes, and dental spirochetes can cause phlegmon. The development of the disease is associated with the deep penetration of the infection into soft tissues, the state of lymph outflow, and the allergic reactivity of the body.
Phlegmon is prone to progression and spread. Pain sensations with phlegmon are permanent. At first they are insignificant, later - growing.
When chewing, the pain becomes sharp, the mobility of the jaw is impaired, swallowing becomes difficult, respiratory and speech functions deteriorate. Asymmetry appears on the face in the form of swelling on the side of the affected gums.
The infection poisons the entire body, therefore, symptoms characteristic of intoxication appear: chills, weakness, sweating, increased breathing and pulse. The temperature may rise up to 40 ° C.
Peri-maxillary phlegmon is treated surgically through incisions, revealing a purulent focus. Next, the pus is removed using rubber or gauze strips. The operation is performed under general anesthesia. The patient is given a large dose of antibiotics. In special cases, the outcome of treatment for this disease is questionable.
The inflammatory process in the oral cavity is developing rapidly. An already dangerous gumboil can cause serious complications, so you should immediately contact your dentist. To temporarily relieve pain, you can take pain relievers, rinse your mouth with antiseptics, or apply a compress to the affected area. It is better to refuse taking antibiotics before the appointment of a specialist.
n
The author of the article: Muravitsky Boris Viktorovich, dentist, especially for the website ayzdorov.ru