2024 Author: Josephine Shorter | [email protected]. Last modified: 2023-12-16 21:43
Blood pH: what is the norm and how to measure it?
The pH, which determines the acidity of the blood, or pH, or a marker of acid-base balance, is a constant value.
Its values are normally in the range from 7.36 to 7.44, usually 7.4 units.
Displacement of indicators towards the alkaline side (alkalosis), or towards acidity (acidosis) are symptoms of trouble that require urgent treatment.
If the pH drops below 7 units, or rises above 7.8 units, a person is in a borderline state between life and death, where 6.8 on the one hand, and 8.0 units from the opposite segment of the range mean the death of the organism.

Content:
- Acid-base balance: what is it?
- How the systems work
- pH of different human blood systems
- Acidosis, blood alkalosis
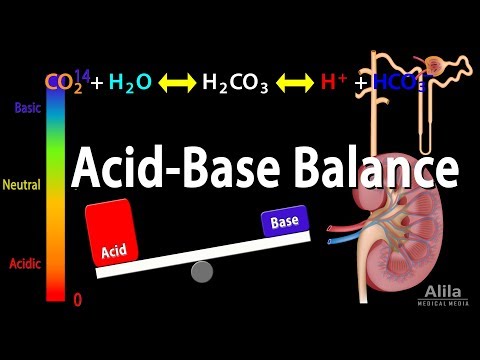
Acid-base balance: what is it?

It would seem that the entry into the digestive tract, and further into the blood, products with an acidic or alkaline reaction should change the composition of the blood. In fact, the body's buffer systems ensure the stability of the acid-base balance, preventing fluctuations outside the safe range.
List of buffer systems:
- Bicarbonate (hydrocarbonate) system - provides at least 50% of the adaptive capabilities of the hemostasis system;
- Hemoglobin system - 35% safety;
- Blood protein system - 10% buffer capacity;
- Phosphate system - 5-6% buffer safety.
These systems, supporting the vital activity of the body, prevent the shift of acid-base balance in any direction, despite the fact that the body consumes foods of various compositions. Buffer systems have an inexhaustible margin of safety, since they are constantly supported by the excretory system, which is activated at the level of reflexes when it is necessary to remove metabolic products.
How the systems work
Basic hydrocarbonate system

The hydrocarbonate system includes two components: H2CO3 and NaHCO3. Chemical reactions constantly occur between them and the acids and alkalis entering the bloodstream.
Strong alkali reaction:
NaOH + H2CO3 → NaHCO3 + H2O
Sodium bicarbonate, formed as a result of this interaction, is soon excreted by the urinary system.
The acid is neutralized as follows:
HCl + NaHCO3 → NaCl + H2CO3
The reaction produces carbon dioxide, which is carried by the lungs into the environment.
The bicarbonate buffering system is most sensitive to pH changes and therefore reacts immediately.
Hemoglobin, protein and phosphate systems of the blood
Blood hemoglobin with the help of red pigment reacts to changes in acidity, binding oxygen, or giving it to the surrounding tissues. The acidity of the red pigment hemoglobin changes by 0.15 units, acting, depending on the circumstances, as a neutral salt or as a weak acid.
The reaction of hemoglobin when an alkaline base enters the blood:
NaOH + HHb → NaHb + H2O
The interaction of hemoglobin when acid enters the blood:
HCl + NaHb → NaCl + HHb
The protein buffering system is involved in maintaining the pH balance depending on the concentration and structure of protein compounds.
The phosphate buffer system maintains the acid-base balance in urine, in the intercellular fluid, and in the cytoplasm of the cell.
pH of different human blood systems
The acid-base index of oxygenated arterial blood is 0.01-0.02 units higher than the same index of venous blood, which contains carbon dioxide in excess.
The acidity of blood plasma, which has a balance of hydrogen ions and hydroxyl ions, corresponds to the acidity of the blood as a whole.
The pH of other media (serum) may have a small range of values. Blood plasma withdrawn from the hemostatic system is devoid of fibrinogen. Its acidity is of practical importance when plasma is used to determine the blood group using hemaglutinating sera.
Blood acidosis and alkalosis

The shift of the hydrogen balance to the acidic or alkaline side can be compensated and uncompensated. It is determined by the alkaline reservoir - the volume of carbon dioxide displaced by a strong acid from 100 ml of plasma. The rate of this indicator is 50-70 ml of CO 2.
- CO 2 below 45 ml - uncompensated acidosis;
- CO 2 above 70 ml - alkalosis.
Alkalosis types:
- Gas - occurs with altitude sickness, with hyperventilation of the lungs, is provoked by an increased release of carbon dioxide by the lungs, goes into hypocapnia;
- Non-gas - distinguish between alimentary alkalosis from food and metabolic alkalosis associated with changes in metabolism.
Types of acidosis:
- Gas - provoked by the slow release of CO 2 from the lungs, goes into hypercapnia;
- Non-gas (alimentary) - occurs with the accumulation of metabolic products, when they come from the digestive tract;
- Primary renal - occurs when there is a violation of reosorption in the renal tubules, accompanied by a loss of alkali.
With a significant deviation of the pH value from the norm, qualified medical assistance is required. When he is in the limit values of the range, with a satisfactory state of health, it is important for the patient himself to pay attention to his state of health.
The main causes of pH disturbances are the use of “harmful” foods, alcohol, and smoking. If the patient does not possess information, he will not pay attention to his health until he is in a state of acute pathology.
It is possible to normalize the acid-base balance with the help of dietary nutrition, but when the previous lifestyle returns, the pH values will return to their previous values.
To maintain the indicator within the normal range, adherence to the rules of a healthy diet, regimen, and the implementation of recreational activities are required.

Author of the article: Alekseeva Maria Yurievna | Therapist
Education: From 2010 to 2016 Practitioner of the therapeutic hospital of the central medical-sanitary unit No. 21, city of elektrostal. Since 2016 she has been working in the diagnostic center No. 3.
Recommended:
Blood Sugar Rate - High And Low Blood Sugar

Blood sugar rateBlood glucose is a sugar that is carried by the bloodstream to all cells in the body to supply them with energy. The body regulates blood glucose levels so that they remain moderate: enough to fuel cells, but not enough to overload blood flow
AST In The Blood - What Is The Norm, The Reasons For The Increase, What Does The AST Blood Test Mean?

Blood test for ASTWhat does AST blood test mean?AST, AST, AST or aspartate aminotransferase - this is the same concept, denoting one of the enzymes of protein metabolism in the body. This enzyme is responsible for the synthesis of amino acids that make up cell membranes and tissues
Blood In The Feces - What To Do If You Find Feces With Blood? Causes Of Occurrence

What to do if you find feces with blood?Blood in the stool is a symptom of a large number of fairly serious diseases. Sometimes this is the only sign of trouble, but more often the appearance of bloody inclusions is accompanied by other manifestations that are not typical for the body in normal conditions
Blood Cancer - Signs, Symptoms, Stages And Treatments For Blood Cancer. Blood Cancer In Children

Signs, symptoms, stages and treatment of blood cancerContent:What is blood cancer?Blood cancer symptomsCauses of blood cancerStage 4 blood cancerBlood cancer in childrenBlood Cancer TreatmentWhat is blood cancer?Blood cancer is a malignant disease that affects and destroys the hematopoietic system
High Blood Pressure - Causes, Signs, Symptoms. What To Do With High Blood Pressure?

High pressureCauses, signs and symptoms of high blood pressureContent:What is pressure?High blood pressure reasonsRisk factorsHigh blood pressure symptomsHigh pressure treatmentWhat to do with high pressure?Complications of high blood pressureWhat is pressure?