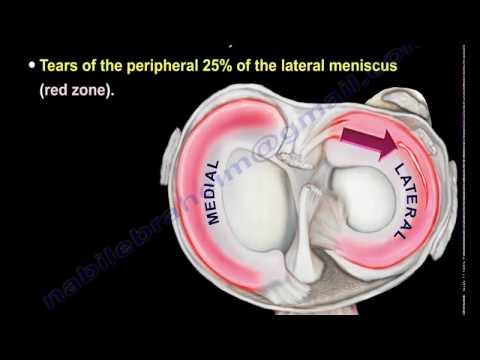
Causes and symptoms of the lateral meniscus of the knee
Related articles:
-

Image -

Image -

Image -

Image -

Image
Definition of disease

Menisci in the knee joint act as shock absorbers, serve for the complete interaction of the shape of the contacting surfaces of the bones and maintain the stability of the knee joint. The lateral meniscus is located outside the knee joint and is more mobile than the medial (internal) meniscus, making it less prone to traumatic injury.
Causes of injury to the lateral meniscus of the knee
The most common cause of lateral meniscus injury is an indirect or combined injury in which the lower leg is inverted inward. With too sharp extension of the leg from a bent state, excessive abduction of the lower leg, damage to the meniscus can also occur.
Direct injury, for example, when the joint directly hits the hard edge of any surface or when struck by a heavy moving object, is rarely diagnosed. But, if it happens repeatedly, then most often chronic trauma to the meniscus develops, which eventually leads to its rupture.
Diseases of a rheumatic nature can cause the development of degenerative changes in the lateral meniscus.
Signs and symptoms of damage to the lateral meniscus
Clinical manifestations of damage to the lateral meniscus are usually divided into two periods: acute and chronic. Often at the onset of the disease it is very difficult to make a correct diagnosis, since there are symptoms of nonspecific inflammation, characteristic of other internal joint injuries. As a rule, the patient is worried about painful sensations in the area of damage, along the joint space. When moving, especially when extending, a sharp pain occurs, which leads to a limitation of motor ability.
In most cases, the injury is instantaneous and leads to bruises, tears, and in severe cases to rupture or even crushing of the meniscus. A complete rupture of the first injured meniscus most often occurs in the presence of degenerative changes or an inflammatory process. As a result of conservative therapy, most patients experience complete recovery.
After the end of the subacute period, which lasts 2-3 weeks, the reactive phenomena disappear, and the true clinical picture of the damage becomes visible. It is characterized by the presence of certain symptoms, such as pain that is constantly present and inflammation of the capsule. The presence of effusion is determined and joint blockage is common. A patient history detailing the details of the injury and positive pain tests for extension, displacement and compression play an important role in making a correct diagnosis.
Diagnosis of damage to the lateral meniscus
A detailed description of the moment of injury is very important for diagnosis. Damage to the lateral meniscus is very rarely accompanied by blockade of the joint, due to its mobility, it is more prone to compression than rupture. As a rule, there are symptoms of movement and slipping of the meniscus and a specific click with minimal movement.
With traumatic damage to the lateral meniscus, patients complain of pain in the area of the external joint gap, the intensity of which increases with the movement of the lower leg inward. Physical examination reveals swelling of the knee joint and the development of infiltration.
These symptoms are quite common and are present in other pathologies of the knee joint, which significantly complicates the diagnosis. Pain tests are most often negative when the lateral meniscus is damaged, except for the clicking knee, joint blockade also does not develop in all cases.
The most objective method is radiography, which is used to determine the narrowing of the damaged part of the joint space with signs of deforming arthrosis.
A certain difficulty arises in the diagnosis if the meniscus has an atypical shape or if both menisci are damaged during chronic trauma.
Treatment of damage to the lateral meniscus
The choice of treatment method depends on the nature of the injury and the patient's condition. Bruises, small tears, changes of the degenerative type are subject to primary conservative treatment. If the injury is serious, with large tears and is accompanied by severe pain or blockage, surgical treatment is categorically indicated, which is most often carried out using endoscopic equipment. Patients who have not improved as a result of conservative treatment are also subject to surgical intervention.
Rehabilitation after injury of the lateral meniscus
The timing and measures for the rehabilitation of the treatment of such diseases are selected individually for each patient. It is recommended at the initial stage to use crutches and to minimize the load on the injured leg.

Article author: Mochalov Pavel Alexandrovich | d. m. n. therapist
Education: Moscow Medical Institute. IM Sechenov, specialty - "General Medicine" in 1991, in 1993 "Occupational Diseases", in 1996 "Therapy".