Diffuse osteoporosis
Content:
- What is diffuse osteoporosis?
- Causes of diffuse osteoporosis
- Invisible process
- Early diagnosis
- Complex therapy
- Preventive measures
What is diffuse osteoporosis?
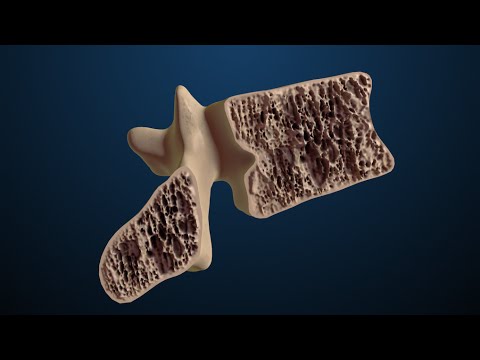
With diffuse osteoporosis, bone tissue becomes thinner all over the body at once. This type of disease usually occurs in old age.
With osteoporosis, the bone tissue does not have time to recover. As a result, bones become very fragile. Even a very small injury can provoke a fracture, and the skeleton begins to deform. This is the most striking manifestation of the disease in general.
In the case of diffuse osteoporosis, there may be no fractures. However, this type of pathology is characterized by aching pains in the spine, sometimes very severe.
And since the entire skeleton weakens, diffuse osteoporosis is also called glassy and uniform. People after fifty are especially susceptible to this disease, but it can also occur in children.
Causes of diffuse osteoporosis

Observations show that diffuse osteoporosis often occurs against the background of malignant neoplasms, for example, myeloma. This is a tumor that develops from the elements of the bone marrow. Its main target is the spine: the bodies and arches of the vertebrae are affected.
One of the most common factors in the development of osteoporosis in women is a decrease in blood levels of the hormone estrogen. The edge, after which a woman finds herself in a high-risk group, is menopause. The body produces less and less female hormones and the processes of bone tissue repair slow down. In other words, calcium is literally "washed away" from the bones, their tissue becomes more rarefied. In men, a lack of the male hormone testosterone can provoke the disease.
The second "helper" in the development of osteoporosis is thyroid disease. They cause failure during the processes of destruction and repair of bone tissue. The risk group also includes people with diabetes.
Another factor in the development of the disease is a violation of the absorption of calcium, which can be a consequence of intestinal pathology. Calcium may simply not be enough in food. And in this case, even with normal functioning of all systems of the body, a person also risks "earning" osteoporosis.
Another risk factor is long-term use of drugs containing glucocorticosteroids and aluminum. As well as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
Diffuse osteoporosis in children can be caused by a genetic predisposition.
Invisible process
At the very beginning, diffuse osteoporosis does not manifest itself in any way. There are no painful sensations. At first glance, such harmless symptoms as curvature of the spine, aching back pain, cramps in the muscles of the legs and feet, decreased performance and fatigue may appear.
And the fact that the progressive loss of bone tissue even without a noticeable deformation of the skeleton can sometimes cause excruciating pain, people usually do not associate with osteoporosis. A person may not even think about the disease.
Early diagnosis
However, the disease can be identified without waiting for serious consequences. Already at the first stages of the development of disorders, ultrasound helps to notice changes in bones and joints. With the help of ultrasound densitometry, osteoporosis is determined with a decrease in bone mass by 2-5 percent.
X-ray “sees” the pathology of bone tissue when twenty-five to thirty percent of its normal mass has already been lost. The image reflects not dense bones, but translucent shadows outlined with a sharper line. Diffuse osteoporosis is characterized by the presence of many thin plates in the bone tissue, with wide gaps between them. On the X-ray you can see how the intervertebral discs seem to be pressed into the vertebral bodies - fish spine syndrome.
To clarify the diagnosis and determine the stage of the disease, dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry and computed tomography are performed.
A blood test is also taken to find out the level of calcium, phosphorus and alkaline phosphatase in it. Together, this makes it possible to compose a complete picture.
Complex therapy

The progression of diffuse osteoporosis can be stopped if the processes of destruction and restoration of bone tissue are brought into balance. For this, calcium preparations are used in combination with vitamin D: without it, calcium cannot be absorbed by the human body. In difficult cases, drugs are used to accelerate the growth of bone tissue and slow down its destruction.
If osteoporosis has developed against the background of another disease, it must be treated. In case this disease is chronic, means are used to reduce its manifestations.
Treatment of osteoporosis in women during menopause may include hormonal therapy: synthetic hormones replace the lack of their own estrogen, and this has a positive effect on the state of bone tissue.
The minimum task is to significantly reduce the rate of bone thinning. The maximum task is to ensure the growth of bone tissue. This should prevent fractures and increase the patient's mobility.
In especially advanced cases of diffuse osteoporosis of the spine, an operation is prescribed using the method of puncture vertebroplasty.
It is important to understand that the treatment of diffuse osteoporosis is a long process, sometimes lasting until the end of life. And its serious part is a special diet, which is made up for each patient individually.
Preventive measures
As a prevention of diffuse and other types of osteoporosis, it is recommended to eat properly. The diet should have enough calcium and vitamin D. But it is better not to drink coffee or drink it only with milk. Adequate physical activity prevents the development of the disease. And quitting tobacco smoking.
In addition, doctors advise keeping your bone density under control. For older people, get regular X-ray or ultrasound densitometry. For women after sixty-five and for men after seventy. Those who are younger should be examined if they are taking medications that have the side effect of a decrease in bone density. And in the presence of thyroid pathologies.

Author of the article: Kaplan Alexander Sergeevich | Orthopedist
Education: diploma in the specialty "General Medicine" received in 2009 at the Medical Academy. I. M. Sechenov. In 2012 completed postgraduate studies in Traumatology and Orthopedics at the City Clinical Hospital named after Botkin at the Department of Traumatology, Orthopedics and Disaster Surgery.