Trachea cancer
Tracheal cancer is a malignant formation that forms in the trachea.
Content:
- Tracheal cancer classification
- Tracheal cancer symptoms
- Tracheal cancer causes
- Tracheal cancer treatment
Tracheal cancer classification
Reveal education of the primary and secondary type. The first of them is formed from the walls of the trachea, is often located close to the bronchi and is a fairly rare pathology, which makes up from 0.1 to 0.2% of all examples of malignant formations. Most prone to the disease are males aged 40 to 60 years.

Much more often formations are formed in the trachea of the secondary type. This occurs as a consequence of the proliferation of formations in conjugated localizations (for example, cancer of the larynx, thyroid gland) or with more distant metastases. You should also highlight the cylinder - a formation that develops from the specific epithelium of the tracheal glands. She is prone to infiltrating growth and the formation of metastases. Determined by slow formation.
Squamous cell carcinoma is a formation that is detected from the tissues of the squamous epithelium. It is located on the wall of the trachea from the side or behind, is determined by a slow rate of increase and begins to appear one or two years after the onset of the development of the disease.
Tracheal sarcoma is formed from the constituent connective tissues. It is more often located at the point of division of the trachea, it can be formed from any formations. The ailment is divided into spindle cell and round cell sarcoma.
A carcinoid is a passively growing mass that arises from the neuroendocrine tissues of the mucosa.
There are also more rare forms of oncology, namely hemangiopericytoma, hemangioendothelioma, malignant neurofibroma.
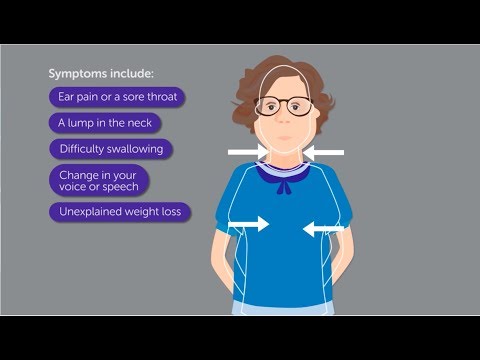
Tracheal cancer symptoms
Manifestations of tracheal cancer depend on the formation, direction of growth, narrowing of the lumen of the trachea:
-
the initial stage passes without symptoms, because the body has already adapted to the systematic narrowing of the trachea and increasing hypoxia;
- primary symptoms are formed with a narrowing of more than two-thirds, while shortness of breath is detected, which increases after physical exertion and with respiratory ailments;
- sleep dysfunction occurs due to choking;
- there are frequent situations when people are faced with a dry, prolonged cough, which is forced by changing the posture of the body. Even experts take such a condition for bronchitis or asthma, as a result of which they stipulate a course precisely for such ailments;
- sputum is detected, if the disintegration of education is diagnosed, then an unpleasant odor will join;
- more than half of patients have streaks or a small amount of blood when sputum is released, they sometimes cough up parts of the tumor. This is accompanied by a relief of respiratory functions;
- in the case of a formation on the back of the trachea, there are complaints of difficulty in the swallowing process.
Tracheal cancer causes

Common causes of tracheal cancer are:
- age category over 40 years. In most cases, people from 40 to 60 years old face the presented ailment, but this age limit is systematically decreasing;
- belonging to the male sex, women suffer from it much less often;
- addiction to smoking also provokes the formation of tracheal cancer due to the ratio of carcinogenic substances;
- genetic predisposition, even if it belongs to less close relatives;
- the presence of a virus such as human papilloma;
- the effect of increased doses of radiation, for example, radiation therapy in the process of treating formations of conjugated organs;
- specific factors: presence of nickel industry, specific dust, asbestos on the nearby territory.
See also: Other Cancer Causes and Risk Factors
Tracheal cancer treatment
The treatment process for this disease is combined: removal of the tumor with further radiation therapy. Such an intervention involves cutting out the formed formation within other cells. With circular spreading, the transverse trachea resection is allowed, after which its ends approach each other and are sutured.
The admissibility of the operation depends solely on the location of the formation: the lower it is, the more difficult it will be to carry out the operation. If it is not possible to completely get rid of the education, then palliative surgery is performed. The most common tracheofissure is performed: the annular parts of the trachea are cut, after which the trachea is removed using either forceps or an electric knife.
- Tracheostomy. If the disease is in a neglected state, then the operation is limited exclusively to the tracheostomy. But this simple operation from a technical point of view in patients who suffer from tracheal cancer can be associated with a whole list of dangers. If the formation occupies a significant part of the organ, in this case you have to breathe through a narrow gap with a specific location of the head. Changing this position and introducing the tube through the formed formations can provoke the death of the patient. In this regard, everything is carried out in a semi-sitting position, and the incision is carried out below the location of the formation.
- Cricotomy. When this seems impossible, the operation begins with a cricotomy: the larynx is cut along the middle line, while visualization of the formation and the place through which a person breathes is feasible. A long tube is inserted into this gap, which goes directly into the bronchi. After that, it is permissible to carry out subsequent manipulations.
- Radiation therapy is the only treatment for such patients whose cancer goes away with a tumor growing into organs and tissues. However, due to the active effect of specific radiation on the chest area during radiation therapy at a distance, the total focal dose should not exceed 60 Gy.
- Chemotherapy is not effective in tracheal oncology, and therefore is not practiced. Thus, it is imperative to detect tracheal cancer early in order to provide treatment that is truly effective.
See also: Other effective treatments

The author of the article: Bykov Evgeny Pavlovich | Oncologist, surgeon
Education: graduated from residency at the Russian Scientific Oncological Center. N. N. Blokhin "and received a diploma in the specialty" Oncologist"