Paralysis
Causes and symptoms of paralysis
What is paralysis?

Paralysis is a serious change in the body that leads to loss and impairment of motor functions. In medicine, paralysis is characterized by its degree of manifestation, persistence and localization. There are complete and partial paralysis, irreversible and transient, widespread and non-widespread. When paralysis is diagnosed in the place opposite to the site of the CNS lesion, it is called crossed or contralateral paralysis.
When a lesion is found on the paralyzed side, they speak of uncrossed or ipsilateral paralysis. According to the degree and localization, paralysis is divided into tetraplegia, monoplegia, hemiplegia and paraplegia. Hemiplegia is a complete paralysis of the face or limbs located on one side of the body. Diplegia refers to bilateral paralysis of one part of the body. Tetraplegia is diagnosed when all four limbs are paralyzed.
Paraplegia is a partial or complete paralysis of both legs, combined with a violation of the motor functions of the lower body due to an illness or injury. Many diseases of the human nervous system can be the harbingers of paralysis. Paralysis does not exist separately as a disease and has many causal factors causing it. Any disturbance in the functioning of the nervous system can lead to damage to motor functions.
Causes of paralysis
Among the organic causes that cause paralysis, there are: traumatic conditions, disseminated encephalomyelitis, infectious diseases (for example, viral encephalitis, various types of tuberculosis, inflammation of the meninges, poliomyelitis), poisoning of the body, metabolic disorders, nutritional disorders, vascular diseases, cancers.
Paralysis can result from hereditary or congenital diseases of the central nervous system. Toxic reasons are: lack of vitamin B1 (beriberi disease), lack of nicotinic acid (pellagra), alcoholic polyneuritis, intoxication of the body with salts of heavy metals (lead). Cerebral palsy (CP) and Erb's palsy are caused by a specific birth trauma.
The list of diseases, the origin of which is unknown, can be the harbingers of paralysis of various directions. Paralysis in wounds and fractures occurs when there is a violation of the motor pathways and centers. There are many cases when paralysis is a consequence of the hysterics of a mentally unhealthy person, then the patient needs the help of a psychiatrist.
Paralysis symptoms
Clinically, some types of paralysis are distinguished, which act as an independent disease. For example, parkinsonism, poliomyelitis, Erb's palsy, Bell's palsy, bulbar and pseudobulbar palsy, cerebral palsy, myoplegia, as well as many congenital and inherited diseases.
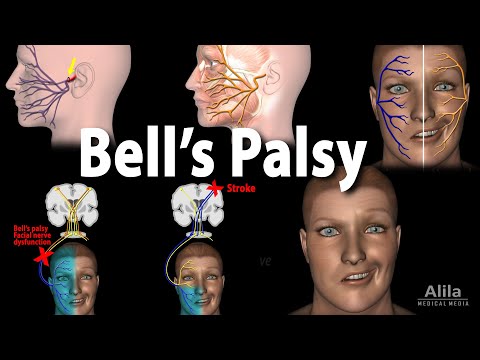
Peripheral paralysis of the face is called Bell's palsy. It occurs when the facial nerve is damaged and is quite widespread. The causes of Bell's palsy are varied: hypothermia, polyneuropathy, infectious diseases (diphtheria, mumps), and cancerous tumors. The main symptoms of the presented disease are severe headaches and migraines.
The disease can be the result of trauma or surgical manipulation of the body. But in many cases, the origin of the disease is unknown. In violation of the motor functions of the facial nerve, complete unilateral muscular paralysis of the face occurs. The patient cannot close his eyes, it is difficult for him to talk and eat. Bilateral damage to the facial nerve is very rare. Death of muscles deprived of movement can occur after 2 weeks. The prognosis and further course of the disease are determined by the cause of the disease.
So paralysis of the facial nerve in case of ear disease or trauma can be irreversible. In many cases of paralysis of the facial nerve, it is possible to restore the functions of the facial muscles after a few weeks.
A type of paralysis - bulbar paralysis is of two types: acute or progressive. Polio is a form of acute bulbar paralysis. The disease disrupts the work of the medulla oblongata and the bridge, there is a paralysis of the tongue and organs of the oral cavity. The onset of the disease is characterized by the following symptoms: headache, dizziness, fever. No muscle pain.
Bulbar paralysis is characterized by the absence of a uniform pulse and respiration. The voice becomes nasal and it is sometimes difficult to make out what the patient says. The patient has difficulty holding food in his mouth, it is poured out. The presence of hemiplegia and monoplegia can often be noted. The course of the disease is rapid, death occurs in a few days. Recovery with partial paralysis is also possible.
The disease with progressive bulbar palsy differs in duration and occurs in middle-aged men. The origin of the disease is unknown. There is a progressive paralysis of the muscles of the oral cavity organs. The symptoms are the same as for acute bulbar palsy. There is no cure, because death occurs in the interval from 1 to 3 years.
Diagnosis of paralysis

Diagnosis of paralysis should include the following points: modern examination of the patient by a neurologist, examination of the body using high-performance computed tomography, full diagnosis of the disease using magnetic resonance imaging, check of reflexes of the legs (for example, knee reflex), obtaining results using neurosonography, and fluoroscopy.
Various diagnostics for the paralysis of the body's motor functions are carried out based on clinical signs and medical research. Examination of the nerves in hemiplegia (paralysis of the face or limbs located on one side of the body) is important in determining the site of the lesion. Such a serious disorder in the motor area of the frontal lobe of the brain occurs along with complete paralysis of the symmetrical side.
Unilateral contraction of the facial muscles is a symptom of multiple sclerosis. If the cervical muscles are involved in the pathological process, then this may be evidenced by the Lehr-Mitt symptom, which manifests itself as a feeling of numbness and tingling of the hands and feet in case of a head tilt.
Sometimes the patient experiences sudden, sharp pain when bending the neck, which spreads down the spine. When determining the location of the primary focus with a brain abscess, the auricles, mastoid processes and paranasal sinuses of the patient are examined.
When Bell's palsy is diagnosed, hearing is tested to determine if the auditory nerve is impaired, and the functioning of the vestibular apparatus is checked by observing the balance of the sick person, lacrimation is monitored, the necessary blood tests are taken and a lumbar puncture is done.
Diagnosing infantile cerebral palsy involves monitoring the child during his first years of life. Differential diagnosis is aimed at detecting various congenital and hereditary diseases by means of scans and various tests. When establishing a diagnosis of cerebral palsy, a thorough neurological examination is necessary.
Paralysis treatment
The main task in the treatment of paralysis is to eliminate the cause of the disease. In all cases, specific symptomatic treatment, gymnastics and therapeutic massage are carried out to help restore motor functions. For each case, the physician individually selects a paralysis treatment program, including drug therapy.
Physiotherapy is the main method of therapy for this dangerous disease. It is very important to position the affected limb correctly. In the case of central paralysis, the patient's arms and legs are positioned so that contractures do not appear. Gymnastics should combine vigorous and passive movements. Passive exercises are carried out with great care, preventing excessive motor activity of the limbs.
With paralysis of the peripheral type, a special massage is done before therapeutic exercises. When movements begin to appear, specific active actions are introduced into the treatment. Remedial gymnastics in combination with a bath or pool is of great benefit.
Special drug therapy is selected individually by a neuropathologist. Inside, proserin, dibazol, intramuscular injection of vitamin B1, melliktin (in case of increased muscle tone) are prescribed. In the treatment of dangerous Bell's palsy, salicylates, corticosteroid drugs and, in addition to drugs, electrotherapy are used.
In the case of drug treatment of bulbar paralysis, a course of vascular therapy is carried out using drugs that can improve metabolic processes in the brain, as well as oxygen therapy. Drugs used in the treatment of spastic paralysis: imidazoline, dantrolene, gabapentin, benzodiazepines. In addition, for spastic paralysis, Botox treatment is used, injecting it into the affected muscles, which then become relaxed. Spastic paralysis is characterized by surgical intervention.
In the treatment of paralysis, long-term stay of the patient in bed can be bad for the course of the disease. Bed rest will cause poor circulation, dizziness and fainting.
It is worth remembering one thing that in the treatment of paralysis it is necessary to constantly move, and if this is an unbearable task for the patient, then you need to help him. The practice of breathing exercises involves all the lungs that are not fully working in case of paralysis.
Prevention of paralysis
Prevention of this disease consists mainly in the prevention of those serious diseases that can cause paralysis.

Article author: Mochalov Pavel Alexandrovich | d. m. n. therapist
Education: Moscow Medical Institute. IM Sechenov, specialty - "General Medicine" in 1991, in 1993 "Occupational Diseases", in 1996 "Therapy".