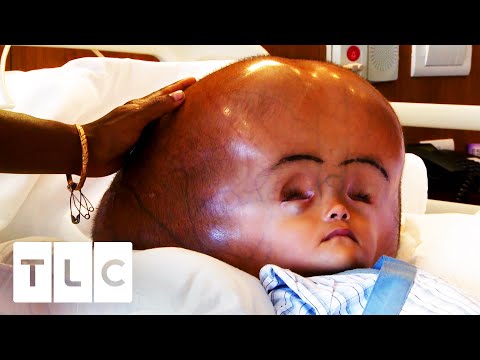
Fibroma in a child

Fibroma is a painless, benign, spherical tumor made of connective tissue. It is located in both single and multiple nodes (fibromatosis). There are congenital fibroids, but more often appear with age. The child usually forms after the age of five.
It is localized in children, as a rule, on the skin of the limbs and trunk, less often on the mucous membranes, in the internal organs and cavities. Reaching a large size, the tumor can disrupt the blood supply to neighboring organs, thereby disrupting their normal functioning. The tumor itself does not ulcerate, does not metastasize, but sometimes it can malignant.
The causes of fibroids in a child are not fully understood. But experts agree that hereditary predisposition is an important factor. There are two types of fibroids: soft and hard.
The optimal method of treatment is the radical removal of the neoplasm, after which, as a rule, its histological examination is carried out. Single nodes after removal extremely rarely give relapses.
Sometimes babies and young children have multiple lumps of fibroids called fibromatosis on different parts of the body. There are the following types of fibromatosis in infants: fibrous hamartoma, gingival fibromatosis, multiple juvenile hyaline fibromatosis, infantile digital fibromatosis, neck fibromatosis.
Fibrous hamartoma in 19% of cases is found in children at the age of one year, in other cases at the age of two to four years, mainly in boys. It affects the limbs, groin, buttocks, armpit. The nodes are yellow-gray. They are a three-component tumor: a fibrous component, mature adipose tissue and fragments of myxoid pitch. Relapses are rare.
Gingival fibromatosis is a hereditary disease. It is extremely rare, usually in conjunction with other hereditary diseases with the same probability in both sexes. It is a tumor-like thickening of the gums. This tumor did not show spontaneous regression. Relapses occur.
Multiple juvenile hyaline fibromatosis affects the soft tissues of predominantly male infants and infants. Localized on the back, knees, head, nose, ears. It is represented by white-gray subcutaneous nodules up to five centimeters in diameter.
Infantile digital fibromatosis is a disease that affects the tips of the feet, hands and fingers of infants, sometimes older children. Single, less often multiple tumors are represented by dense nodes in the dermis with a diameter of two to three millimeters.
Fibromatosis of the neck is a rare disease in which connective tissue replaces the sternocleidomastoid muscle. The cause may be heredity (family pathology) or a complication of rheumatism with neck lesions. The knots are several centimeters in diameter.
For children under the age of ten, the operation is performed under anesthesia. In older adults, surgery can be performed under local anesthesia.
Fibroma of the lungs
Fibroma among all benign lung neoplasms was recorded in 1-2% of cases. The disease affects both the left and right lungs with equal probability. It is more common in men. Localization is usually peripheral.
The tumor is usually small in size, several centimeters. However, it happens that the neoplasm grows to an enormous size, occupying 50% of the chest cavity. Peripheral nodes are sometimes located on a narrow stem. Reliable data on malignancy of pulmonary fibroids have not been found.
Visually, the tumor is a whitish dense knot with a smooth, even surface. The mucous membrane covering the fibroma may be ulcerated.
The causes of pulmonary fibroids are not fully understood. It is believed that one of the main factors is genetic predisposition. Many experts also claim that the following factors increase the likelihood of a benign tumor: smoking, viruses, mutations, poor ecology.
There are three stages of development of benign lung neoplasms: preclinical (asymptomatic) stage, initial clinical and severe clinical stage. At the last stage, the patient may experience chest pain, shortness of breath, pulmonary bleeding, impaired bronchial patency.
Treatment of pulmonary fibroids is exclusively surgical. Surgical intervention is advisable to be carried out as early as possible, which allows you to prevent malignancy of the tumor, avoid the start of irreversible processes, and carry out the most sparing operation to remove it.

Article author: Mochalov Pavel Alexandrovich | d. m. n. therapist
Education: Moscow Medical Institute. IM Sechenov, specialty - "General Medicine" in 1991, in 1993 "Occupational Diseases", in 1996 "Therapy".