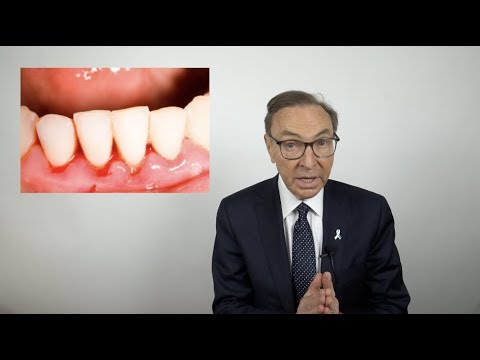
Bleeding gums
Content:
- What is bleeding gums?
- Causes of bleeding gums
- How to stop bleeding gums?
- How to rinse the gums when bleeding?
What is bleeding gums?
Bleeding gums is the systematic discharge of small amounts of blood while eating or brushing teeth, usually accompanied by periodontal inflammation. The stronger the inflammatory process, the more blood will be released from the gums. In some cases, blood appears even when the gums are at rest, for example, at night.
This problem is very common. According to statistics, every inhabitant of the planet has encountered it at least once. However, not everyone pays due attention to bleeding gums, which can subsequently lead to more serious health problems.
Causes of bleeding gums

The following reasons can be distinguished leading to bleeding gums:
- Poor oral hygiene. This is one of the simplest causes of blood. Gums can be injured when the toothbrush is too hard. It is enough to replace it, and the problem will be fixed;
- Dental calculus. Formation that appears on the surface of the tooth at the junction with the gum. The stone irritates delicate tissues with its sharp edges, which causes the gums to bleed. Tartar is formed as a result of poor cleaning of the teeth, and soft plaque, mixing with the enzymes contained in saliva, turns into hard;
- Inflammatory gum disease. These are gingivitis, periodontitis and periodontal disease. If a person has catarrhal periodontitis, then in addition to bloody discharge from the gums, he has a distortion of taste and swelling of the gums. If treatment is delayed or absent, the disease will lead to tooth loss;
-
Pregnancy can cause bleeding gums. This is due to a hormonal disruption in the woman's body. Similar changes are reflected in the vessels in the gums. As a result, periodontal tissues become looser, sometimes very edematous and vulnerable. Blood can be released even with the usual touch of the gums;
- Hematological disorders, that is, blood diseases;
- Removal of a tooth. Normally, blood can be released for a couple of hours, but no more. This is a natural process that occurs when the gum has been injured. If bleeding lasts longer or occurs some time after the procedure, you should consult a doctor;
- Oral cavity trauma;
- Pyogenic granuloma is a benign formation that looks like a tumor. If it occurs on the gums, it most often bleeds;
- Teething that puts pressure on the gums, injuring them. A similar phenomenon is typical for children, when milk teeth are cut and then replaced, and for middle-aged people, when wisdom teeth appear;
- Lack of vitamins in the body;
- Inflammatory diseases of the nasopharynx and ears.;
- Epulis is a tumor formation that appears on the gum;
- Long-term treatment with certain medications. These include, for example, aspirin, which is familiar to many people. Bleeding gums when taken is a common side effect.
How to stop bleeding from the gums?

In order to stop the bleeding from the gums, it is necessary to understand the cause that caused it. To do this, you need to visit the dentist and check the oral cavity, be sure to inform the doctor about your problem. He can prescribe a special toothpaste for the prevention and treatment of a disease that caused bleeding from the gums, or a mouthwash that helps relieve the inflammatory process in the gums, and therefore eliminate their bleeding.
There are also creams and gels for bleeding gums, for example:
- Metrogyl Denta;
- Holisal;
- Solcoseryl.
You can supplement the main therapeutic course with rinsing with various decoctions of medicinal plants. For example, oak bark, shepherd's purse, nettle, chamomile, water pepper, etc. These herbs are proven to be effective and are often prescribed by dentists as a complementary treatment.
For bleeding gums, disinfectants and anti-inflammatories such as:
- Miramistin;
- Maraslavin;
- Malavit.
They are used locally; they should not be taken internally. Also, in addition to the main treatment, you need to take care of good oral hygiene. To do this, you need to change your toothbrush to a softer one and rinse after each meal. The food should not be too hard, so as not to further injure the sore gums.
Special attention should be paid to the situation when bleeding does not go away for a long time after tooth extraction. If blood does not appear immediately, but after a while, then this may become an indirect sign of low coagulability. Using medication to relieve pain during tooth extraction can also cause bleeding. To stop the discharge of blood from the gums, you need to put a sterile gauze swab on it and leave it in your mouth for 20 minutes.
If, after tooth extraction, after some time there is intense bleeding, then most often this indicates that the vessel has been damaged, and a medical examination is necessary. Before going to the doctor, you can apply ice to the face area from the side of the extracted tooth. This will narrow blood vessels and relieve swelling.
Sometimes bleeding after tooth extraction occurs against a background of increased pressure. Hypertension should be reported to the dentist so that sedatives are administered before the procedure if necessary.
As a prevention of bleeding gums, it is important to regularly visit the dentist for an examination of the state of the oral cavity and teeth. Professional cleaning and the use of quality toothpastes are also required.
How to rinse your gums with bleeding?
Depending on what caused the problem, a mouthwash will be selected by the dentist.
Remedies for bleeding gums include:
- Stomatofit;
- Angilex;
- Givalex;
- Stomatidin.
Sometimes doctors prescribe such a widely known and well-known drug as Chlorhexidine. This antiseptic is applied topically in the form of rinsing, or in the form of lotions.
Strongly brewed oak bark has a powerful astringent property. It can be used at the first signs of bleeding gums.
Table salt has antibacterial properties, so it can be used for gum disease. Baking soda works in a similar way, but both agents can only muffle the pathological process. For a complete treatment of bleeding gums, medications prescribed by a dentist are required.
n
The author of the article: Muravitsky Boris Viktorovich, dentist, especially for the website ayzdorov.ru