Aphthous stomatitis
Aphthous stomatitis is not only unpleasant, but also quite painful. Ulcers that form in the mouth make it difficult to eat. You should not independently treat aphthous stomatitis with traditional medicine. This can be not only dangerous, but also threatens the transition of the disease into a chronic form.
Aphthous stomatitis has several varieties. To clarify the diagnosis and start the correct treatment, you need to see a doctor.
Content:
- What is aphthous stomatitis?
- Causes of aphthous stomatitis
- Symptoms of aphthous stomatitis
- Disease stages
- Classification of the disease
- Diagnostics
- Treatment of aphthous stomatitis
- Prevention
What is aphthous stomatitis?
Aphthous stomatitis is an inflammation of a portion of the oral mucosa. On it, the so-called aphthae are formed, that is, small ulcers of white color. Each ulcer is surrounded by a red rim. Aphthae can be oval and round. Sometimes they form one at a time, and sometimes several. The main symptom of the disease is pain and burning sensation in the mouth. These unpleasant symptoms become more intense with meals. Aphthae heals for a long time, the recovery time for damaged tissues can be extended by 10-14 days. After the aphthae disappear, healthy, intact mucosa will remain in their place.
You can get rid of the usual aphthous stomatitis completely. In the chronic form of the disease, it will only be possible to achieve long-term remission. This will be considered a success. The treatment approach must be comprehensive. In addition to medicines, you can use traditional medicine methods, but only after consulting a doctor. If therapy is absent for a long time, then acute aphthous stomatitis will become chronic and will constantly recur. Infection with aphthous stomatitis occurs in a household way.

Most often, sores appear on the inside of the cheeks and lips. This is due to the fact that these places are more prone to injury. Scratches and bite marks may appear on the mucous membranes. On the tongue, ulcers can also form, but this happens less often. Sometimes aphthous stomatitis leads to an increase in body temperature and increased weakness. Normally, the oral cavity should be cleansed in 8-10 days.
Causes of aphthous stomatitis

To date, the reasons for the formation of aphthae in the mouth are unknown. Doctors speculate that there is a link between the disease and the state of the immune system. At some point, the immune system ceases to recognize the molecules of its own saliva, begins to actively produce lymphocytes against them, which leads to the formation of ulceration sites.
Often, aphthae are formed when there is a focus of chronic infection in the body. It can focus on the tonsils, throat, and digestive tract.
Risk factors that increase the likelihood of aft formation in the oral cavity include:
- Change of climatic zones.
- Difficult working conditions that overload a person both emotionally and physically.
- Prolonged stress and frequent emotional distress.
In general, any factors affecting the state of the immune system can cause aphthous stomatitis. The lower the body's resistance, the higher the likelihood of stomatitis.
Symptoms of aphthous stomatitis

Symptoms will vary depending on the stage of the disease.
When aphthous stomatitis has just begun to develop, this process is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Weakness, deterioration in health.
- Decreased appetite.
- Increased body temperature. Typically, it stays within 38 ° C.
- An increase in lymph nodes in size. This process may involve the cervical, submandibular and occipital plexuses.
- The appearance of areas of redness in the mouth.
If aphthae appear on the tongue, then this gives the person special discomfort. They not only hurt, but also contribute to increased salivation, as well as distortion of taste. The process of eating is complicated.
Disease stages

There are several stages of development of aphthous stomatitis:
- Initial stage. During this period, the patient's body temperature rises, general health worsens, lymph nodes swell, appetite disappears.
- Second stage. Reddish painful areas appear in the mouth, in the place of which ulcers form later.
- The stage of the main manifestations of stomatitis. Ulcers reach 5 mm in size, have a gray-white color. At this time, the increased body temperature and general malaise persist.
- Ulcer resolution stage. The defect is cleared of plaque, after which it disappears. At this stage, all unpleasant symptoms of the disease begin to fade away.
The average duration of aphthous stomatitis is 8-16 days. After this time, the mucous membrane of the oral cavity is restored, there are no scars or scars on it. This is the norm. However, if a person develops a deforming form of aphthous stomatitis, then after the resolution of ulcerative defects, the soft tissues of the lips and inner surface of the cheeks may slightly change.
Classification of the disease
Aphthous stomatitis is divided into 2 types: acute and chronic.

Acute stomatitis is called acute gingivostomatitis. It is caused by viral infections. At the same time, the person's body temperature rises, the lymph nodes become inflamed. The ulcers hurt and cause a burning sensation in the mouth. Discomfort during eating increases. At the same time, appetite decreases, overall health worsens.
As for the chronic form of stomatitis, its causes today remain unexplored. Doctors suggest that adenoviruses provoke the formation of aft. It is believed that this problem is of an autoimmune nature. Other experts insist that stomatitis is caused by special staphylococci. However, the chronic form of the disease is always diagnosed in people with weak immune systems.
Chronic stomatitis rarely leads to an increase in body temperature. Most often it remains normal, as do the lymph nodes. The ulcers heal quickly, within 2-7 days.
By itself, aphthous stomatitis has several varieties. Depending on this, its symptoms will differ:
- Fibrinous. With fibrinous stomatitis, ulcerative defects, covered with a grayish coating, form in the oral cavity. They heal in 1-2 weeks. In the future, the disease may recur. This happens throughout the year. Then exacerbations occur more often. If there is no treatment, then the person will constantly experience symptoms of stomatitis.
- Necrotic. Necrotizing stomatitis is associated with severe diseases of the body. In the area of inflammation, cells begin to die off. At first, the ulcers do not hurt, but as they grow, the person begins to experience serious discomfort. Such defects heal over a long time - from 2 weeks to a month.
- Glandular. Glandular stomatitis has a relationship with the salivary glands. The ulcers hurt a lot and take a long time to heal. Moreover, even with proper therapy, the process of restoring mucous membranes is delayed.
- Scarring. With a scarring form of stomatitis, small ulcerative defects form in the mouth. They grow rapidly in size and can reach 3 cm in diameter. After their resolution, scar tissue remains on the mucous membranes. Treatment should be long-term, since this form of the disease is considered one of the most difficult.
- Deforming. The disease has a severe course. Ulcers with deforming stomatitis are large, poorly amenable to drug correction. After recovery, scars remain on the mucous membranes that can deform them.
Diagnostics
You need to visit your dentist to make a diagnosis. If an ulcer has formed in a child, then you need to go to a pediatric dentist. As a rule, determining the form of the disease is not difficult, since aphthous stomatitis has characteristic symptoms. A general examination of the oral cavity is sufficient for the doctor. To find out the cause of the violation, you will need to donate blood for general and biochemical analysis.
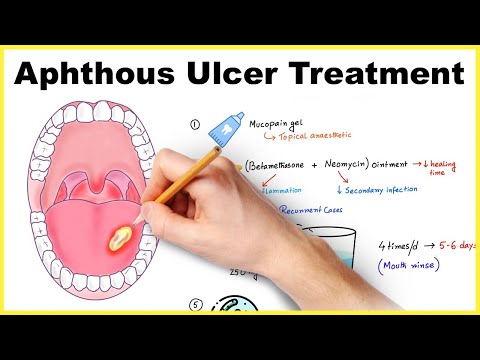
Treatment of aphthous stomatitis

Treatment of stomatitis includes the treatment of the oral cavity with medications. For this, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory agents are used that destroy pathogenic flora and accelerate the recovery process. Sometimes oral medications are required, but the doctor must prescribe them. An indispensable component of therapy is rinsing the mouth with drugs.
Drugs that can be used in the treatment of stomatitis:
- Stomatofit. This product contains sage, oak bark, chamomile extract and essential oils. Together, they have anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effects. The stomatophyte is dissolved in water and rinsed with it.
- Miramistin. A powerful antiseptic that destroys most of the pathogenic flora. This allows for faster tissue repair. If antibacterial agents are used to treat stomatitis, then Miramistin enhances their effect. They can irrigate the affected areas or simply rinse your mouth.
- Chlorhexidine. It is an antiseptic used to rinse the mouth. It perfectly disinfects mucous membranes and destroys microbial flora.
- Furacilin solution and hydrogen peroxide. These products are used to rinse the mouth.
If aphthae cause pain to a person, then you need to use analgesics.
The following drugs have an analgesic effect:
- Metrogyl Denta. This is a dental gel that kills bacteria and reduces inflammation. It is applied to the affected area with a thin layer.
- Holisal. This drug destroys microbes, relieves the inflammatory reaction. It is produced in the form of a gel, quickly penetrates into tissues and numbes the affected area.
- Kamistad. The drug contains Lidocaine, which has a pronounced analgesic effect. In addition, the drug promotes the speedy cleansing of aft and the restoration of mucous membranes.
A patient with aphthous stomatitis can be prescribed medicinal sprays: Ingalipt, Lugol, Lidocaine Asept, etc. The choice of a specific drug remains with the dentist. In addition to the main treatment, the doctor may recommend taking antipyretic, antiviral and antihistamines.
Sometimes patients with aphthous stomatitis need to take sedatives or tranquilizers. They are used to treat people under stress or with diagnosed nervous exhaustion.
To increase the body's defenses, the intake of B vitamins and vitamin C, as well as immunomodulators and immunostimulants, is required.
Video: Life is great! Aphthous stomatitis:
Prevention

To prevent the development of aphthous stomatitis, you need to adhere to the following recommendations:
- Monitor the cleanliness of the oral cavity. If the child is small, in order to properly care for his teeth, parents should help him with this.
- Hands should be washed regularly.
- Food must be clean.
- It is necessary to treat all infections in time and sanitize chronic foci of inflammation.
- You should eat right and strengthen your immune system.
- You need to quit smoking and drinking alcohol. Even inhalation of tobacco smoke causes harm to the body.
- Prevention of viral diseases should be dealt with.
- You need to visit the dentist every 3 months.

Article author: Mochalov Pavel Alexandrovich | d. m. n. therapist
Education: Moscow Medical Institute. IM Sechenov, specialty - "General Medicine" in 1991, in 1993 "Occupational Diseases", in 1996 "Therapy".